Characterization of transcriptional regulatory domains of ankyrin repeat cofactor-1
- PMID: 17521611
- PMCID: PMC1950474
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.017
Characterization of transcriptional regulatory domains of ankyrin repeat cofactor-1
Abstract
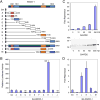
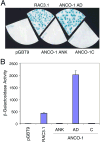
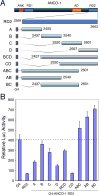
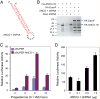
The ankyrin repeats cofactor-1 (ANCO-1) was recently identified as a p160 coactivator-interacting protein that may inhibit transcriptional activity of nuclear receptors. Here, we have characterized the transcriptional regulatory domains of ANCO-1. Two intrinsic repression domains (RD) were identified: an N-terminal RD1 at residues 318-611 and a C-terminal RD2 at 2369-2663. ANCO-1 also contains an activation domain (AD) capable of stimulating transcription in both mammalian and yeast cells. The minimal AD was delimited to a 70-amino acid region at residues 2076-2145. Overall, full-length ANCO-1 exhibited transcriptional repressor activity, suggesting that RD domains may suppress the AD activity. We further demonstrated that ANCO-1 silencing by siRNA enhanced progesterone receptor-mediated transcription. Together, these results indicate that the transcriptional potential of ANCO-1 may be modulated by a combination of repression and activation signals.
Figures

References
-
- Chen JD, Evans RM. A transcriptional co-repressor that interacts with nuclear hormone receptors. Nature. 1995;377:454–457. [see comments] - PubMed
-
- Horlein AJ, Naar AM, Heinzel T, Torchia J, Gloss B, Kurokawa R, Ryan A, Kamei Y, Soderstrom M, Glass CK, et al. Ligand-independent repression by the thyroid hormone receptor mediated by a nuclear receptor co-repressor. Nature. 1995;377:397–404. - PubMed
-
- Nagy L, Kao HY, Chakravarti D, Lin RJ, Hassig CA, Ayer DE, Schreiber SL, Evans RM. Nuclear receptor repression mediated by a complex containing SMRT, mSin3A, and histone deacetylase. Cell. 1997;89:373–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

