Histone modifications around individual BDNF gene promoters in prefrontal cortex are associated with extinction of conditioned fear
- PMID: 17522015
- PMCID: PMC2216532
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.500907
Histone modifications around individual BDNF gene promoters in prefrontal cortex are associated with extinction of conditioned fear
Abstract
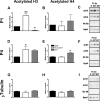
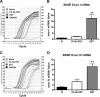
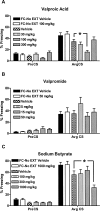
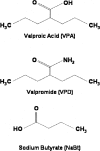
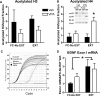
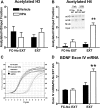
Extinction of conditioned fear is an important model both of inhibitory learning and of behavior therapy for human anxiety disorders. Like other forms of learning, extinction learning is long-lasting and depends on regulated gene expression. Epigenetic mechanisms make an important contribution to persistent changes in gene expression; therefore, in these studies, we have investigated whether epigenetic regulation of gene expression contributes to fear extinction. Since brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is crucial for synaptic plasticity and for the maintenance of long-term memory, we examined histone modifications around two BDNF gene promoters after extinction of cued fear, as potential targets of learning-induced epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Valproic acid (VPA), used for some time as an anticonvulsant and a mood stabilizer, modulates the expression of BDNF, and is a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor. Here, we report that extinction of conditioned fear is accompanied by a significant increase in histone H4 acetylation around the BDNF P4 gene promoter and increases in BDNF exon I and IV mRNA expression in prefrontal cortex, that VPA enhances long-term memory for extinction because of its HDAC inhibitor effects, and that VPA potentiates the effect of weak extinction training on histone H4 acetylation around both the BDNF P1 and P4 gene promoters and on BDNF exon IV mRNA expression. These results suggest a relationship between histone H4 modification, epigenetic regulation of BDNF gene expression, and long-term memory for extinction of conditioned fear. In addition, they suggest that HDAC inhibitors may become a useful pharmacological adjunct to psychotherapy for human anxiety disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Barad M., Blouin A.M., Cain C.K. Like extinction, latent inhibition of conditioned fear in mice is blocked by systemic inhibition of L-type voltage-gated calcium channels. Learn. Mem. 2005;11:536–539. - PubMed
-
- Baum M. Spontaneous recovery from the effects of flooding (exposure) in animals. Behav. Res. Ther. 1988;26:185–186. - PubMed
-
- Berman D.E., Dudai Y. Memory extinction, learning anew, and learning the new: Dissociations in the molecular machinery of learning in cortex. Science. 2001;291:2417–2419. - PubMed
-
- Bouton M.E., King D.A. Contextual control of the extinction of conditioned fear: Tests for the associative value of the context. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 1983;9:248–265. - PubMed
-
- Cain C.K., Blouin A.M., Barad M. Temporally massed CS presentations generate more fear extinction than spaced presentations. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 2003;29:323–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
