Hippocampal regulation of context-dependent neuronal activity in the lateral amygdala
- PMID: 17522021
- PMCID: PMC2216537
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.477007
Hippocampal regulation of context-dependent neuronal activity in the lateral amygdala
Abstract
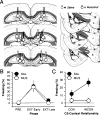
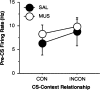
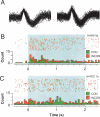
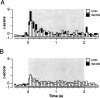
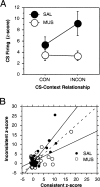
Pavlovian fear conditioning is a robust and enduring form of emotional learning that provides an ideal model system for studying contextual regulation of memory retrieval. After extinction the expression of fear conditional responses (CRs) is context-specific: A conditional stimulus (CS) elicits greater conditional responding outside compared with inside the extinction context. Dorsal hippocampal inactivation with muscimol attenuates context-specific CR expression. We have previously shown that CS-elicited spike firing in the lateral nucleus of the amygdala is context-specific after extinction. The present study examines whether dorsal hippocampal inactivation with muscimol disrupts context-specific firing in the lateral amygdala. We conditioned rats to two separate auditory CSs and then extinguished each CS in separate and distinct contexts. Thereafter, single-unit activity and conditional freezing were tested to one CS in both extinction contexts after saline or muscimol infusion into the dorsal hippocampus. After saline infusion, rats froze more to the CS when it was presented outside of its extinction context, but froze equally in both contexts after muscimol infusion. In parallel with the behavior, lateral nucleus neurons exhibited context-dependent firing to extinguished CSs, and hippocampal inactivation disrupted this activity pattern. These data reveal a novel role for the hippocampus in regulating the context-specific firing of lateral amygdala neurons after fear memory extinction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hippocampal inactivation disrupts contextual retrieval of fear memory after extinction.J Neurosci. 2001 Mar 1;21(5):1720-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-05-01720.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11222661 Free PMC article.
-
Context-dependent neuronal activity in the lateral amygdala represents fear memories after extinction.J Neurosci. 2003 Sep 10;23(23):8410-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-23-08410.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12968003 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal inactivation disrupts the acquisition and contextual encoding of fear extinction.J Neurosci. 2005 Sep 28;25(39):8978-87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2246-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16192388 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal signalling of fear memory.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004 Nov;5(11):844-52. doi: 10.1038/nrn1535. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15496862 Review.
-
Neural circuits involved in the renewal of extinguished fear.IUBMB Life. 2017 Jul;69(7):470-478. doi: 10.1002/iub.1636. Epub 2017 May 2. IUBMB Life. 2017. PMID: 28464461 Review.
Cited by
-
Gating of fear in prelimbic cortex by hippocampal and amygdala inputs.Neuron. 2012 Nov 21;76(4):804-12. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.028. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 23177964 Free PMC article.
-
BEHAVIORAL AND NEUROBIOLOGICAL MECHANISMS OF PAVLOVIAN AND INSTRUMENTAL EXTINCTION LEARNING.Physiol Rev. 2021 Apr 1;101(2):611-681. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00016.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Physiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 32970967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obligatory roles of dopamine D1 receptors in the dentate gyrus in antidepressant actions of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, fluoxetine.Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Jun;25(6):1229-1244. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0316-x. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Mol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 30531938 Free PMC article.
-
Transcranial Electric Stimulation and the Extinction of Fear.Clin Psychol. 2020 Fall;73(4):5-14. Clin Psychol. 2020. PMID: 35153300 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Bidirectional changes in the intrinsic excitability of infralimbic neurons reflect a possible regulatory role in the acquisition and extinction of Pavlovian conditioned fear.J Neurosci. 2008 Jul 16;28(29):7245-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2130-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18632927 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Barrientos R.M., O’Reilly R.C., Rudy J.W. Memory for context is impaired by injecting anisomycin into dorsal hippocampus following context exploration. Behav. Brain Res. 2002;134:299–306. - PubMed
-
- Bouton M.E. Context, time, and memory retrieval in the interference paradigms of Pavlovian learning. Psychol. Bull. 1993;114:80–99. - PubMed
-
- Bouton M.E., Bolles R.C. Contextual control of the extinction of conditioned fear. Learn. Motiv. 1979;10:445–466.
-
- Bouton M.E., Westbrook R.F., Corcoran K.A., Maren S. Contextual and temporal modulation of extinction: Behavioral and biological mechanisms. Biol. Psychiatry. 2006;60:352–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
