Coupled translation of the second open reading frame of M2 mRNA is sequence dependent and differs significantly within the subfamily Pneumovirinae
- PMID: 17522208
- PMCID: PMC1951343
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00457-07
Coupled translation of the second open reading frame of M2 mRNA is sequence dependent and differs significantly within the subfamily Pneumovirinae
Abstract
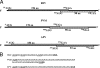
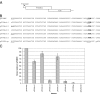
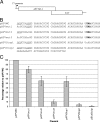
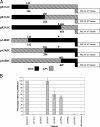
Coupled translation, first described in the M2 gene of pneumovirus respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), is an alternative mechanism of translational initiation in which the ribosomes which translate the first (M2-1) open reading frame (ORF) move a short distance upstream after termination and reinitiate translation from a second (M2-2) overlapping ORF. Here, we show that the same mechanism occurs in two closely related viruses, avian pneumovirus (APV) and pneumonia virus of mice (PVM), although with markedly different efficiencies. To identify the reasons for the variation in efficiency of coupled expression between RSV and APV, we used chimeric M2-1 genes containing different lengths of the M2-1 ORF from each virus. An essential component allowing coupled expression in the chimeras was a segment from the RSV M2-1 coding region containing a high degree of secondary structure. Additional sequences at the 5' end of the RSV M2-1 ORF also promoted coupled translation when the region with high levels of secondary structure was present. These data indicate that at least two distant parts of the mRNA transcript, together with a suitable overlapping region, are involved in the coupling process. Replacement of the last 102 nucleotides of the RSV M2-1 ORF with the equivalent APV sequence showed identical levels of coupled translation. Thus, the overlapping region can direct the ribosome back onto the start codon of the second ORF while the upstream coding sequence of the M2-1 ORF determines the levels of coupled expression.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmadian, G., P. Chambers, and A. J. Easton. 1999. Detection and characterization of proteins encoded by the second ORF of the M2 gene of pneumoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 80:2011-2016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

