The cofilin pathway in breast cancer invasion and metastasis
- PMID: 17522712
- PMCID: PMC4270061
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc2148
The cofilin pathway in breast cancer invasion and metastasis
Abstract
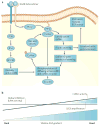
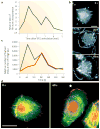
Recent evidence indicates that metastatic capacity is an inherent feature of breast tumours and not a rare, late acquired event. This has led to new models of metastasis. The interpretation of expression-profiling data in the context of these new models has identified the cofilin pathway as a major determinant of metastasis. Recent studies indicate that the overall activity of the cofilin pathway, and not that of any single gene within the pathway, determines the invasive and metastatic phenotype of tumour cells. These results predict that inhibitors directed at the output of the cofilin pathway will have therapeutic benefit in combating metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chemotaxis: Cofilin in the driver's seat.Curr Biol. 2006 Dec 19;16(24):R1030-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.11.011. Curr Biol. 2006. PMID: 17174909
-
The mitotic kinase Aurora-A induces mammary cell migration and breast cancer metastasis by activating the Cofilin-F-actin pathway.Cancer Res. 2010 Nov 15;70(22):9118-28. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1246. Epub 2010 Nov 2. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21045147
-
JG6, a novel marine-derived oligosaccharide, suppresses breast cancer metastasis via binding to cofilin.Oncotarget. 2014 Jun 15;5(11):3568-78. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1959. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25003327 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of cofilin in development and its mechanisms of regulation.Dev Growth Differ. 2015 May;57(4):275-90. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12213. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Dev Growth Differ. 2015. PMID: 25864508 Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and breast cancer metastasis.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015 Jan;16(1):32-43. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1400221. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015. PMID: 25559953 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabinoid receptor CB2 is involved in tetrahydrocannabinol-induced anti-inflammation against lipopolysaccharide in MG-63 cells.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:362126. doi: 10.1155/2015/362126. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25653478 Free PMC article.
-
RhoJ modulates melanoma invasion by altering actin cytoskeletal dynamics.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013 Mar;26(2):218-25. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12058. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013. PMID: 23253891 Free PMC article.
-
Neuregulin mediates F-actin-driven cell migration through inhibition of protein kinase D1 via Rac1 protein.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 4;288(1):455-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.397448. Epub 2012 Nov 12. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23148218 Free PMC article.
-
Subcellular distribution and expression of cofilin and ezrin in human colon adenocarcinoma cell lines with different metastatic potential.Eur J Histochem. 2010 Apr 13;54(2):e14. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2010.e14. Eur J Histochem. 2010. PMID: 20558337 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of regulatory targets of alternative isoforms of the epidermal growth factor receptor in a glioblastoma cell line.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Aug 22;20(1):434. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2944-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31438847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liotta LA, Kohn EC. The microenvironment of the tumour-host interface. Nature. 2001;411:375–379. - PubMed
-
- Condeelis J, Segall JE. Intravital imaging of cell movement in tumours. Nature Rev Cancer. 2003;3:921–930. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani A, Giavazzi R, Alessandri G, Spreafico F, Gerattini S. Characterization of tumor lines derived from spontaneous metastases of transplanted murine sarcoma. Eur J Cancer. 1981;17:71–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

