Lung ischemia-reperfusion injury: implications of oxidative stress and platelet-arteriolar wall interactions
- PMID: 17522980
- PMCID: PMC3182489
- DOI: 10.1080/13813450601118976
Lung ischemia-reperfusion injury: implications of oxidative stress and platelet-arteriolar wall interactions
Abstract
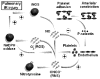
Pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury may result from trauma, atherosclerosis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary thrombosis and surgical procedures such as cardiopulmonary bypass and lung transplantation. IR injury induces oxidative stress characterized by formation of reactive oxygen (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). Nitric oxide (NO) overproduction via inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) is an important component in the pathogenesis of IR. Reaction of NO with ROS forms RNS as secondary reactive products, which cause platelet activation and upregulation of adhesion molecules. This mechanism of injury is particularly important during pulmonary IR with increased iNOS activity in the presence of oxidative stress. Platelet-endothelial interactions may play an important role in causing pulmonary arteriolar vasoconstriction and post-ischemic alveolar hypoperfusion. This review discusses the relationship between ROS, RNS, P-selectin, and platelet-arteriolar wall interactions and proposes a hypothesis for their role in microvascular responses during pulmonary IR.
Figures
References
-
- Adkins WK, Taylor AE. Role of xanthine oxidase and neutrophils in ischemia–reperfusion injury in rabbit lung. J Appl Physiol. 1990;69:2012–8. - PubMed
-
- Al Mehdi A, Zhao G, Dodia C, Tozawa K, Costa K, Muzykantov V, Ross C, Blecha F, Dinauer M, Fisher A. Endothelial NADPH oxidase as the source of oxidants in lungs exposed to ischemia or high K+ Circ Res. 1998a;83:730–7. - PubMed
-
- Al Mehdi A, Zhao G, Fisher A. ATP-independent membrane depolarization with ischemia in the oxygen-ventilated isolated rat lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998b;18:653–61. - PubMed
-
- Al-Majed A, Khattab M, Raza M, Al-Shabanah O, Mostafa A. Potentiation of diclofenac-induced anti-inflammatory response by aminoguanidine in carrageenan-induced acute inflammation in rats: The role of nitric oxide. Inflamm Res. 2003;52(9):378–82. - PubMed
-
- Al-Mehdi A, Shuman H, Fisher A. Intracellular generation of reactive oxygen species during nonhypoxic lung ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:L294–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
