Stimulation of phospholipase Cbeta by membrane interactions, interdomain movement, and G protein binding--how many ways can you activate an enzyme?
- PMID: 17524618
- PMCID: PMC1963342
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.04.006
Stimulation of phospholipase Cbeta by membrane interactions, interdomain movement, and G protein binding--how many ways can you activate an enzyme?
Abstract
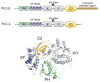
Signaling proteins are usually composed of one or more conserved structural domains. These domains are usually regulatory in nature by binding to specific activators or effectors, or species that regulate cellular location, etc. Inositol-specific mammalian phospholipase C (PLC) enzymes are multidomain proteins whose activities are controlled by regulators, such as G proteins, as well as membrane interactions. One of these domains has been found to bind membranes, regulators, and activate the catalytic region. The recently solved structure of a major region of PLC-beta2 together with the structure of PLC-delta1 and a wealth of biochemical studies poises the system towards an understanding of the mechanism through which their regulations occurs.
Figures
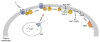



References
-
- Patterson RL, van Rossum DB, Nikolaidis N, Gill DL, Snyder SH. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30(12):688–697. - PubMed
-
- Bunney TD, Katan M. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16(12):640–648. - PubMed
-
- Swann K, Saunders CM, Rogers NT, Lai FA. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2006;17(2):264–273. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson KM, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Sigler PB. Cell. 1995;83(6):1037–1046. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

