Drinking social norms and drinking behaviours: a multilevel analysis of 137 workgroups in 16 worksites
- PMID: 17525095
- PMCID: PMC2092559
- DOI: 10.1136/oem.2006.031765
Drinking social norms and drinking behaviours: a multilevel analysis of 137 workgroups in 16 worksites
Abstract
Background: Previous studies on worksite drinking norms showed individually perceived norms were associated with drinking behaviours.
Objective: To examine whether restrictive drinking social norms shared by workgroup membership are associated with decreased heavy drinking, frequent drinking and drinking at work at the worker level.
Methods: The sample included 5338 workers with complete data nested in 137 supervisory workgroups from 16 American worksites. Multilevel models were fitted to examine the association between workgroup drinking norms and heavy drinking, frequent drinking and drinking at work.
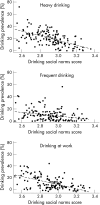
Results: Multivariate adjusted models showed participants working in workgroups in the most discouraging drinking norms quartile were 45% less likely to be heavy drinkers, 54% less likely to be frequent drinkers and 69% less likely to drink at work than their counterparts in the most encouraging quartile.
Conclusions: Strong associations between workgroup level restrictive drinking social norms and drinking outcomes suggest public health efforts at reducing drinking and alcohol-related injuries, illnesses and diseases should target social interventions at worksites.
References
-
- Room R, Babor T, Rehm J. Alcohol and public health. Lancet 2005365519–530. - PubMed
-
- Harwood H J, Fountain D, Fountain G. Economic cost of alcohol and drug abuse in the united states, 1992: a report. Addiction 199994631–635. - PubMed
-
- Ames G M, Janes C. A cultural approach to conceptualizing alcohol and the workplace. (cover story). Alcohol Health & Research World 199216112
-
- Trice H M, Sonnenstuhl W J. On the construction of drinking norms in work organizations. J Stud Alcohol 199051201–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical