Interferon-gamma sensitizes resistant Ewing's sarcoma cells to tumor necrosis factor apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of caspase-8 without altering chemosensitivity
- PMID: 17525260
- PMCID: PMC1899433
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060993
Interferon-gamma sensitizes resistant Ewing's sarcoma cells to tumor necrosis factor apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of caspase-8 without altering chemosensitivity
Abstract
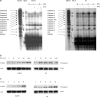
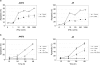
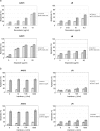
Ewing's sarcoma cells are highly susceptible to apoptosis via tumor necrosis factor apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). Resistance to TRAIL has been linked to deficient expression of caspase-8 in vitro. Here, we report on the status of caspase-8 expression in tumors from patients with Ewing's sarcoma, the effect of interferon-gamma on caspase-8 expression and apoptosis, and the role of caspase-8 for TRAIL- and chemotherapy-mediated apoptosis in Ewing's sarcoma. Using immunohistochemistry, we show that low expression of caspase-8 is seen in about 24% of tumors. Interferon-gamma induces expression of caspase-8 at concentrations achievable in humans and sensitizes cells to TRAIL. Transfection of wild type but not mutant caspase-8 into caspase-8-deficient Ewing's sarcoma cells restored sensitivity to TRAIL, indicating that up-regulation of caspase-8 is sufficient to restore TRAIL sensitivity. In contrast, no role for caspase-8 in chemotherapy-induced apoptosis was identified, because 1) transfection of caspase-8 or treatment with interferon-gamma did not alter the sensitivity of caspase-8-deficient cells to chemotherapeutics, 2) application of chemotherapy did not select for caspase-8-negative tumor cells in vivo, and 3) the caspase-8 status of tumors did not influence survival after chemotherapy-based protocols. In conclusion, our data provide a rationale for the inclusion of interferon-gamma in upcoming clinical trials with TRAIL.
Figures





References
-
- Abadie A, Besancon F, Wietzerbin J. Type I interferon and TNFalpha cooperate with type II interferon for TRAIL induction and triggering of apoptosis in SK-N-MC EWING tumor cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:4911–4920. - PubMed
-
- Thiele CJ. Biology of pediatric peripheral neuroectodermal tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1991;10:311–319. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins D, Barnett T, Bensinger W, Gooley T, Sanders J. Busulfan, melphalan, and thiotepa with or without total marrow irradiation with hematopoietic stem cell rescue for poor-risk Ewing-Sarcoma-Family tumors. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2000;34:328–337. - PubMed
-
- Paulussen M, Ahrens S, Braun-Munzinger G, Craft AW, Dockhorn-Dworniczak B, Dorffel W, Dunst J, Frohlich B, Gobel U, Haussler M, Klingebiel T, Koscielniak E, Mittler U, Rube C, Winkelmann W, Voute PA, Zoubek A, Jurgens H. [EICESS 92 (European Intergroup Cooperative Ewing’s Sarcoma Study): preliminary results]. Klin Padiatr. 1999;211:276–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

