Hypothalamic resistin induces hepatic insulin resistance
- PMID: 17525801
- PMCID: PMC1868785
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI30440
Hypothalamic resistin induces hepatic insulin resistance
Abstract
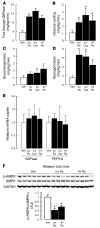
Circulating resistin stimulates endogenous glucose production (GP). Here, we report that bi-directional changes in hypothalamic resistin action have dramatic effects on GP and proinflammatory cytokine expression in the liver. The infusion of either resistin or an active cysteine mutant in the third cerebral ventricle (icv) or in the mediobasal hypothalamus stimulated GP independent of changes in circulating levels of glucoregulatory hormones. Conversely, central antagonism of resistin action markedly diminished the ability of circulating resistin to enhance GP. We also report that centrally mediated mechanisms partially control resistin-induced expression of TNF-alpha, IL-6, and SOCS-3 in the liver. These results unveil what we believe to be a novel site of action of resistin on GP and inflammation and suggest that hypothalamic resistin action can contribute to hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures


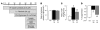

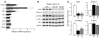
References
-
- Adams K.F., et al. Overweight, obesity, and mortality in a large prospective cohort of persons 50 to 71 years old. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;355:763–778. - PubMed
-
- Ogden C.L., et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999-2004. JAMA. 2006;295:1549–1555. - PubMed
-
- Flier J.S. Obesity wars: molecular progress confronts an expanding epidemic. Cell. 2004;116:337–350. - PubMed
-
- Boden G., et al. Free fatty acids produce insulin resistance and activate the proinflammatory nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in rat liver. Diabetes. 2005;54:3458–3465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 DK072876/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK045024/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37-DK48321/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24-DK071030/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK55758/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK048321/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK45024/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA112023/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK071030/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21-DK075887/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK048321/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK075887/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055758/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32-DK072876/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112023/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

