KAAS: an automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server
- PMID: 17526522
- PMCID: PMC1933193
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm321
KAAS: an automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server
Abstract
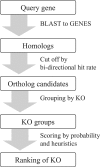
The number of complete and draft genomes is rapidly growing in recent years, and it has become increasingly important to automate the identification of functional properties and biological roles of genes in these genomes. In the KEGG database, genes in complete genomes are annotated with the KEGG orthology (KO) identifiers, or the K numbers, based on the best hit information using Smith-Waterman scores as well as by the manual curation. Each K number represents an ortholog group of genes, and it is directly linked to an object in the KEGG pathway map or the BRITE functional hierarchy. Here, we have developed a web-based server called KAAS (KEGG Automatic Annotation Server: http://www.genome.jp/kegg/kaas/) i.e. an implementation of a rapid method to automatically assign K numbers to genes in the genome, enabling reconstruction of KEGG pathways and BRITE hierarchies. The method is based on sequence similarities, bi-directional best hit information and some heuristics, and has achieved a high degree of accuracy when compared with the manually curated KEGG GENES database.
Figures

References
-
- Smith T, Waterman M. Identification of common molecular subsequences. J. Mol. Biol. 1981;147:195–197. - PubMed
-
- Lipman D, Pearson W. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985;227:1435–1441. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E, Lipman D. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Rost B. Enzyme Function Less Conserved than Anticipated. J. Mol. Biol. 2002;318:595–608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

