Detection and correction of blinking bias in image correlation transport measurements of quantum dot tagged macromolecules
- PMID: 17526586
- PMCID: PMC1929051
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.106864
Detection and correction of blinking bias in image correlation transport measurements of quantum dot tagged macromolecules
Abstract
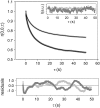
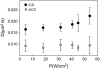
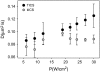
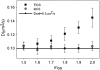
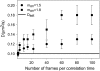
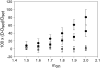
Semiconductor nanocrystals or quantum dots (QDs) are becoming widely used as fluorescent labels for biological applications. Here we demonstrate that fluorescence fluctuation analysis of their diffusional mobility using temporal image correlation spectroscopy is highly susceptible to systematic errors caused by fluorescence blinking of the nanoparticles. Temporal correlation analysis of fluorescence microscopy image time series of streptavidin-functionalized (CdSe)ZnS QDs freely diffusing in two dimensions shows that the correlation functions are fit well to a commonly used diffusion decay model, but the transport coefficients can have significant systematic errors in the measurements due to blinking. Image correlation measurements of the diffusing QD samples measured at different laser excitation powers and analysis of computer simulated image time series verified that the effect we observe is caused by fluorescence intermittency. We show that reciprocal space image correlation analysis can be used for mobility measurements in the presence of blinking emission because it separates the contributions of fluctuations due to photophysics from those due to transport. We also demonstrate application of the image correlation methods for measurement of the diffusion coefficient of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins tagged with QDs as imaged on living fibroblasts.
Figures


References
-
- Bruchez, M. Jr., M. Moronne, P. Gin, S. Weiss, and A. P. Alivisatos. 1998. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science. 281:2013–2016. - PubMed
-
- Alivisatos, P. 2004. The use of nanocrystals in biological detection. Nat. Biotechnol. 22:47–52. - PubMed
-
- Wu, X. Y., J. H. Liu, Q. J. Liu, N. K. Haley, A. J. Treadway, P. J. Larson, F. N. Ge, F. Peale, and P. M. Bruchez. 2002. Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 21:41–46. - PubMed
-
- Pellegrino, T., L. Manna, S. Kudera, T. Liedl, D. Koktysh, L. A. Rogach, S. Keller, J. Rädler, G. Natile, and W. J. Parak. 2004. Hydrophobic nanocrystals coated with an amphiphilic polymer shell: a general route to water soluble nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 4:703–707.
-
- Gao, X., Y. Cui, M. R. Levenson, K. W. L. Chung, and S. Nie. 2004. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 22:969–976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

