Depth-resolved measurement of transient structural changes during action potential propagation
- PMID: 17526590
- PMCID: PMC1929037
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.106.091298
Depth-resolved measurement of transient structural changes during action potential propagation
Abstract
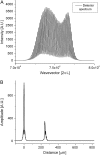
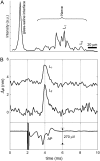
We report noncontact optical measurement of fast transient structural changes in the crustacean nerve during action potential propagation without the need for exogenous chemicals or reflection coatings. The technique, spectral domain optical coherence tomography, provides real-time cross-sectional images of the nerve with micron-scale resolution to select a specific region for functional assessment and interferometric phase sensitivity for subnanometer-scale motion detection. Noncontact optical measurements demonstrate nanometer-scale transient movement on a 1-ms timescale associated with action potential propagation in crayfish and lobster nerves.
Figures


References
-
- Cohen, L. B. 1973. Changes in neuron structure during action potential propagation and synaptic transmission. Physiol. Rev. 53:373–418. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, L. B., R. D. Keynes, and B. Hille. 1968. Light scattering and birefringence changes during nerve activity. Nature. 218:438–441. - PubMed
-
- von Muralt, A. 1975. The optical spike. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. B270:411–423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

