Characterization of the fucosylation pathway in the biosynthesis of glycopeptidolipids from Mycobacterium avium complex
- PMID: 17526707
- PMCID: PMC1951812
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00344-07
Characterization of the fucosylation pathway in the biosynthesis of glycopeptidolipids from Mycobacterium avium complex
Abstract
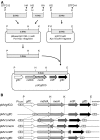
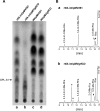
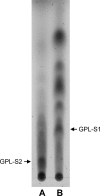
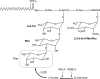
The cell envelopes of several species of nontuberculous mycobacteria, including the Mycobacterium avium complex, contain glycopeptidolipids (GPLs) as major glycolipid components. GPLs are highly antigenic surface molecules, and their variant oligosaccharides define each serotype of the M. avium complex. In the oligosaccharide portion of GPLs, the fucose residue is one of the major sugar moieties, but its biosynthesis remains unclear. To elucidate it, we focused on the 5.0-kb chromosomal region of the M. avium complex that includes five genes, two of which showed high levels of similarity to the genes involved in fucose synthesis. For the characterization of this region by deletion and expression analyses, we constructed a recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis strain that possesses the rtfA gene of the M. avium complex to produce serovar 1 GPL. The results revealed that the 5.0-kb chromosomal region is responsible for the addition of the fucose residue to serovar 1 GPL and that the three genes mdhtA, merA, and gtfD are indispensable for the fucosylation. Functional characterization revealed that the gtfD gene encodes a glycosyltransferase that transfers a fucose residue via 1-->3 linkage to a rhamnose residue of serovar 1 GPL. The other two genes, mdhtA and merA, contributed to the formation of the fucose residue and were predicted to encode the enzymes responsible for the synthesis of fucose from mannose based on their deduced amino acid sequences. These results indicate that the fucosylation pathway in GPL biosynthesis is controlled by a combination of the mdhtA, merA, and gtfD genes. Our findings may contribute to the clarification of the complex glycosylation pathways involved in forming the oligosaccharide portion of GPLs from the M. avium complex, which are structurally distinct.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Mycobacterium avium complex gtfTB gene encodes a glucosyltransferase required for the biosynthesis of serovar 8-specific glycopeptidolipid.J Bacteriol. 2008 Dec;190(24):7918-24. doi: 10.1128/JB.00911-08. Epub 2008 Oct 10. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18849433 Free PMC article.
-
The mycobacterial glycopeptidolipids: structure, function, and their role in pathogenesis.Glycobiology. 2008 Nov;18(11):832-41. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwn076. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Glycobiology. 2008. PMID: 18723691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and characterization of the genes involved in glycosylation pathways of mycobacterial glycopeptidolipid biosynthesis.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jan;188(1):86-95. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.1.86-95.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16352824 Free PMC article.
-
Structural characterization of a specific glycopeptidolipid containing a novel N-acyl-deoxy sugar from mycobacterium intracellulare serotype 7 and genetic analysis of its glycosylation pathway.J Bacteriol. 2007 Feb;189(3):1099-108. doi: 10.1128/JB.01471-06. Epub 2006 Nov 22. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17122347 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of mycobacterium glycopeptidolipids from comparative genomics perspective.J Cell Biochem. 2013 Aug;114(8):1705-13. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24515. J Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23444081 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the genetic bases of the structural diversity of phenolic glycolipids in strains of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 30;283(22):15177-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710275200. Epub 2008 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18390543 Free PMC article.
-
The Mycobacterium avium complex gtfTB gene encodes a glucosyltransferase required for the biosynthesis of serovar 8-specific glycopeptidolipid.J Bacteriol. 2008 Dec;190(24):7918-24. doi: 10.1128/JB.00911-08. Epub 2008 Oct 10. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18849433 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of MSMEG_0412 gene drastically affects surface related properties of Mycobacterium smegmatis.BMC Microbiol. 2016 Nov 8;16(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0888-z. BMC Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27825305 Free PMC article.
-
The mycobacterial glycopeptidolipids: structure, function, and their role in pathogenesis.Glycobiology. 2008 Nov;18(11):832-41. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwn076. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Glycobiology. 2008. PMID: 18723691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel rhamnosyltransferase involved in biosynthesis of serovar 4-specific glycopeptidolipid from Mycobacterium avium complex.J Bacteriol. 2010 Nov;192(21):5700-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.00554-10. Epub 2010 Sep 3. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20817766 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aspinall, G. O., D. Chatterjee, and P. J. Brennan. 1995. The variable surface glycolipids of mycobacteria: structures, synthesis of epitopes, and biological properties. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 51:169-242. - PubMed
-
- Bardarov, S., S. Bardarov, Jr., M. S. Pavelka, Jr., V. Sambandamurthy, M. Larsen, J. Tufariello, J. Chan, G. Hatfull, and W. R. Jacobs, Jr. 2002. Specialized transduction: an efficient method for generating marked and unmarked targeted gene disruptions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis BCG, and M. smegmatis. Microbiology 148:3007-3017. - PubMed
-
- Belisle, J. T., K. Klaczkiewicz, P. J. Brennan, W. R. Jacobs, Jr., and J. M. Inamine. 1993. Rough morphological variants of Mycobacterium avium. Characterization of genomic deletions resulting in the loss of glycopeptidolipid expression. J. Biol. Chem. 268:10517-10523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

