Changes in qnr prevalence and fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Enterobacter spp. collected from 1990 to 2005
- PMID: 17526754
- PMCID: PMC1932512
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00256-07
Changes in qnr prevalence and fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Enterobacter spp. collected from 1990 to 2005
Abstract
Clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Enterobacter spp. collected from 1990 through 2005 at a tertiary care center were studied for qnr genes. Isolates bearing these genes emerged in the mid-1990s, coinciding with the time of a rapid increase in fluoroquinolone resistance. Sixty percent of these isolates were ciprofloxacin susceptible by CLSI breakpoints.
Figures
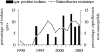

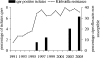
References
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2007. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 15th informational supplement (M100-S17). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
-
- Gay, K., A. Robicsek, J. Strahilevitz, C. H. Park, G. Jacoby, T. J. Barrett, F. Medalla, T. M. Chiller, and D. C. Hooper. 2006. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance in non-Typhi serotypes of Salmonella enterica. Clin. Infect. Dis. 43:297-304. - PubMed
-
- Martínez-Martínez, L., A. Pascual, and G. A. Jacoby. 1998. Quinolone resistance from a transferable plasmid. Lancet 351:797. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

