A genome-wide association study identifies alleles in FGFR2 associated with risk of sporadic postmenopausal breast cancer
- PMID: 17529973
- PMCID: PMC3493132
- DOI: 10.1038/ng2075
A genome-wide association study identifies alleles in FGFR2 associated with risk of sporadic postmenopausal breast cancer
Abstract
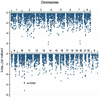
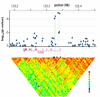
We conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of breast cancer by genotyping 528,173 SNPs in 1,145 postmenopausal women of European ancestry with invasive breast cancer and 1,142 controls. We identified four SNPs in intron 2 of FGFR2 (which encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase and is amplified or overexpressed in some breast cancers) that were highly associated with breast cancer and confirmed this association in 1,776 affected individuals and 2,072 controls from three additional studies. Across the four studies, the association with all four SNPs was highly statistically significant (P(trend) for the most strongly associated SNP (rs1219648) = 1.1 x 10(-10); population attributable risk = 16%). Four SNPs at other loci most strongly associated with breast cancer in the initial GWAS were not associated in the replication studies. Our summary results from the GWAS are available online in a form that should speed the identification of additional risk loci.
Figures
References
-
- Pharoah PD, et al. Polygenic susceptibility to breast cancer and implications for prevention. Nat Genet. 2002;31:33–36. - PubMed
-
- Risch HA, et al. Population BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation frequencies and cancer penetrances: a kin-cohort study in Ontario, Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:1694–1706. - PubMed
-
- Hirschhorn JN, Daly MJ. Genome-wide association studies for common diseases and complex traits. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:95–108. - PubMed
-
- Sladek R, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2007;445:881–885. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA050385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA067262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01CA098233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA87969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA49449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA067262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA065725/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA67262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA098233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA50385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA098710/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA65725/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

