Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 governs learning and synaptic plasticity via control of NMDAR degradation
- PMID: 17529984
- PMCID: PMC3910113
- DOI: 10.1038/nn1914
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 governs learning and synaptic plasticity via control of NMDAR degradation
Abstract
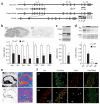
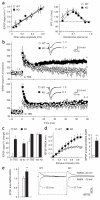
Learning is accompanied by modulation of postsynaptic signal transduction pathways in neurons. Although the neuronal protein kinase cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) has been implicated in cognitive disorders, its role in learning has been obscured by the perinatal lethality of constitutive knockout mice. Here we report that conditional knockout of Cdk5 in the adult mouse brain improved performance in spatial learning tasks and enhanced hippocampal long-term potentiation and NMDA receptor (NMDAR)-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents. Enhanced synaptic plasticity in Cdk5 knockout mice was attributed to reduced NR2B degradation, which caused elevations in total, surface and synaptic NR2B subunit levels and current through NR2B-containing NMDARs. Cdk5 facilitated the degradation of NR2B by directly interacting with both it and its protease, calpain. These findings reveal a previously unknown mechanism by which Cdk5 facilitates calpain-mediated proteolysis of NR2B and may control synaptic plasticity and learning.
Figures
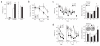
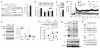
References
-
- Sweatt JD. Mechanisms of Memory. Elsevier; San Diego, California: 2003.
-
- Whitlock JR, Heynen AJ, Shuler MG, Bear MF. Learning induces long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Science. 313:1093–1097. - PubMed
-
- Bibb JA, et al. Effects of chronic exposure to cocaine are regulated by the neuronal protein Cdk5. Nature. 2001;410:376–380. - PubMed
-
- Bibb JA, et al. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 by Cdk5 modulates dopamine signalling in neurons. Nature. 1999;402:669–671. - PubMed
-
- Cheung ZH, Fu AKY, Ip NY. Synaptic roles of Cdk5: implications in higher cognitive functions and neurodegenerative diseases. Neuron. 2006;50:13–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

