Stat3 is tyrosine-phosphorylated through the interleukin-6/glycoprotein 130/Janus kinase pathway in breast cancer
- PMID: 17531096
- PMCID: PMC1929096
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr1680
Stat3 is tyrosine-phosphorylated through the interleukin-6/glycoprotein 130/Janus kinase pathway in breast cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) is constitutively tyrosine-phosphorylated in approximately 50% of primary breast carcinomas. A number of different mechanisms responsible for Stat3 activation, including abnormal activation of receptor tyrosine kinases, Src, and Janus kinases (Jaks), have been implicated in breast cancer.
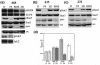
Methods: We examined six breast cancer-derived cell lines expressing high or low levels of tyrosine-phosphorylated Stat3 (pStat3) as well as primary breast cancer specimens.
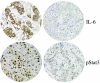
Results: Inhibition of Src or EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) tyrosine kinases had no effect on pStat3 levels, whereas pan-Jak inhibitor P6 resulted in complete abrogation of Stat3 phosphorylation and inhibition of growth. Jaks are required for cytokine signaling, and the glycoprotein 130 (gp130) receptor-associated Jaks are known mediators of Stat3 phosphorylation. Blockade of the gp130 receptor or sequestration of the interleukin-6 (IL-6) ligand led to a decrease of pStat3 levels. Conditioned media from those cell lines expressing high levels of pStat3 contained IL-6 and were capable of stimulating Stat3 phosphorylation. We examined IL-6 levels in primary breast tumors and found a positive correlation between pStat3 and IL-6 expression.
Conclusion: In summary, a principal mechanism of Stat3 activation in breast cancer is through the IL-6/gp130/Jak pathway.
Figures



References
-
- Yu H, Jove R. The STATs of cancer – new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:97–105. - PubMed
-
- Leslie K, Lang C, Devgan G, Azare J, Berishaj M, Gerald W, Kim YB, Paz K, Darnell JE, Albanese C, et al. Cyclin D1 is transcriptionally regulated by and required for transformation by activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Cancer Res. 2006;66:2544–2552. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2203. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

