Impact of cytogenetics on outcome of de novo and therapy-related AML and MDS after allogeneic transplantation
- PMID: 17531775
- PMCID: PMC2743535
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2007.01.079
Impact of cytogenetics on outcome of de novo and therapy-related AML and MDS after allogeneic transplantation
Abstract
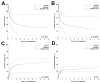
Cytogenetics has an important impact on the prognosis of patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). However, it is unclear whether currently accepted cytogenetic risk groups, which were established for patients treated mostly with standard therapy, are optimally discriminating for patients undergoing HSCT. Also, the impact of cytogenetics in the growing population of patients with therapy-related disease has not been completely elucidated. In this study, we retrospectively analyzed data on 556 patients with AML or MDS transplanted at our institution. We examined, in multivariate analyses, the contribution of cytogenetics to survival, relapse, and nonrelapse mortality for the 476 patients with de novo disease. We used these results to establish an optimal cytogenetic grouping scheme. We then applied this grouping scheme to the 80 patients with therapy-related disease. Our proposed 3-group cytogenetic classification outperformed the established grouping schemes for both de novo and therapy-related disease. When classified by this new scheme, cytogenetics was the strongest prognostic factor for overall survival in our cohort, through its impact on the risk of relapse (and not on nonrelapse mortality). After accounting for cytogenetics, patients with therapy-related AML or MDS had an equivalent outcome to those with de novo disease. This study demonstrates the impact of cytogenetics on the risk of relapse and death for patients with both de novo and therapy-related disease undergoing transplantation; it also emphasizes the necessity of using cytogenetics to stratify patients entering clinical trials, and provides a system for doing so, which can be validated in a multi-institutional database.
Figures
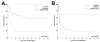
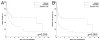
Similar articles
-
Cytomegalovirus Reactivation after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Relapse in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Who Survived to Day 100 after Transplantation: The Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Transplantation-related Complication Working Group.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015 Nov;21(11):2008-16. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2015.07.019. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015. PMID: 26211985
-
Cytogenetic Evolution in Myeloid Neoplasms at Relapse after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Association with Previous Chemotherapy and Effect on Survival.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017 May;23(5):782-789. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28189903
-
Treosulfan, fludarabine, and 2-Gy total body irradiation followed by allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014 Apr;20(4):549-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014. PMID: 24440648 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Myelodysplastic syndrome in children: differentiation from acute myeloid leukemia with a low blast count.Leukemia. 1997 Feb;11(2):206-11. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2400558. Leukemia. 1997. PMID: 9009082 Review.
-
Myelodysplastic syndromes complicating hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Cancer Treat Res. 2001;108:169-84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-1463-3_10. Cancer Treat Res. 2001. PMID: 11702599 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The Secondary Myelodysplastic Neoplasms (MDS) Jigsaw.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 26;15(5):1483. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051483. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody-drug conjugates plus Janus kinase inhibitors enable MHC-mismatched allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.J Clin Invest. 2021 Dec 15;131(24):e145501. doi: 10.1172/JCI145501. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 34730109 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for MDS.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2010 Apr;24(2):407-22. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2010.02.003. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2010. PMID: 20359634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes after radiation therapy are similar to de novo disease and differ from other therapy-related myeloid neoplasms.J Clin Oncol. 2012 Jul 1;30(19):2340-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.7340. Epub 2012 May 14. J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22585703 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term follow-up of patients with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation after primary induction failure.Blood Cancer J. 2023 Dec 10;13(1):179. doi: 10.1038/s41408-023-00953-0. Blood Cancer J. 2023. PMID: 38071327 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bloomfield CD, Goldman A, Hassfeld D, de la Chapelle A. Fourth International Workshop on Chromosomes in Leukemia 1982: Clinical significance of chromosomal abnormalities in acute nonlymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984;11:332–350. - PubMed
-
- Walker H, Smith FJ, Betts DR. Cytogenetics in acute myeloid leukaemia. Blood Rev. 1994;8:30–36. - PubMed
-
- Grimwade D, Moorman A, Hills R, et al. Impact of karyotype on treatment outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2004;83 Suppl 1:S45–48. - PubMed
-
- Heim S. Cytogenetic findings in primary and secondary MDS. Leuk Res. 1992;16:43–46. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 1997;89:2079–2088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

