Mallory body formation is associated with epigenetic phenotypic change in hepatocytes in vivo
- PMID: 17531972
- PMCID: PMC3315395
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2007.03.003
Mallory body formation is associated with epigenetic phenotypic change in hepatocytes in vivo
Abstract
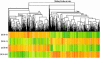
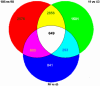
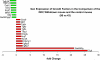
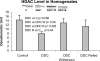
Microarrays were done on the livers of mice fed DDC for 10 weeks, withdrawn 1 month (DDC primed livers) and refed 6 days, and compared with mice fed the control diet. The expression of a large number of genes changed when DDC was fed or refed. A Venn diagram analysis identified 649 genes where gene expression was changed in the same direction. The epigenetic memory of the DDC primed liver involved an increase in the expression of ubiquitin D, alpha fetoprotein, connective tissue growth factor, integrin beta 2, DNA methyl transferase 3a and DNA damage-inducible 45 gamma. DNA methyl transferase 3b was down-regulated as was Cbp/p300. When DDC was refed, DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase were up-regulated as shown by microarray analysis. Histone3 lysine9 acetylation was increased by DDC and DDC refeeding and DNA methyltransferases were not changed as shown by Western blot analysis. The data suggest the concept that the epigenetic memory that explains why DDC primed hepatocytes form MBs in 7 days of DDC refeeding is primarily the result of epigenetic modifications of gene expression through changes in histone acetylation and methylation, as well as DNA methylation.
Figures






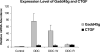

References
-
- Bardag-Gorce F, van Leewen FW, Nguyen V, French BA, Li J, Riley NE, McPhaul LW, Lue YH, French SW. The role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in the formation of Mallory bodies. Exp Mol Pathol. 2002;73:75–83. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- French BA, van Leeuwen F, Riley NE, Yuan QX, Bardag-Gorce F, Lue YH, Marceau N, French SW. Aggresome formation in liver cells in response to different toxic mechanisms. Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and the frameshift mutant of ubiquitin. Exp Mol Pathol. 2001;71:241–246. - PubMed
-
- Gupta M, Gupta SK, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA. Gadd45a and Gadd45b protect hematopoietic cells from UV-induced apoptosis via distinct signaling pathways, including p38 activation and JNK inhibition. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:17552–17558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

