The nonstructural protein 8 (nsp8) of the SARS coronavirus interacts with its ORF6 accessory protein
- PMID: 17532020
- PMCID: PMC7103355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.04.029
The nonstructural protein 8 (nsp8) of the SARS coronavirus interacts with its ORF6 accessory protein
Abstract
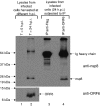
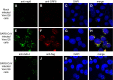
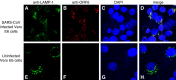
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus (SARS-CoV) caused a severe outbreak in several regions of the world in 2003. The SARS-CoV genome is predicted to contain 14 functional open reading frames (ORFs). The first ORF (1a and 1b) encodes a large polyprotein that is cleaved into nonstructural proteins (nsp). The other ORFs encode for four structural proteins (spike, membrane, nucleocapsid and envelope) as well as eight SARS-CoV-specific accessory proteins (3a, 3b, 6, 7a, 7b, 8a, 8b and 9b). In this report we have cloned the predicted nsp8 gene and the ORF6 gene of the SARS-CoV and studied their abilities to interact with each other. We expressed the two proteins as fusion proteins in the yeast two-hybrid system to demonstrate protein-protein interactions and tested the same using a yeast genetic cross. Further the strength of the interaction was measured by challenging growth of the positive interaction clones on increasing gradients of 2-amino trizole. The interaction was then verified by expressing both proteins separately in-vitro in a coupled-transcription translation system and by coimmunoprecipitation in mammalian cells. Finally, colocalization experiments were performed in SARS-CoV infected Vero E6 mammalian cells to confirm the nsp8-ORF6 interaction. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of the interaction between a SARS-CoV accessory protein and nsp8 and our findings suggest that ORF6 protein may play a role in virus replication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus accessory proteins 6 and 9b interact in vivo.Virus Res. 2012 Oct;169(1):282-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2012.07.012. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Virus Res. 2012. PMID: 22820404 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus ORF7a Inhibits Bone Marrow Stromal Antigen 2 Virion Tethering through a Novel Mechanism of Glycosylation Interference.J Virol. 2015 Dec;89(23):11820-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02274-15. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26378163 Free PMC article.
-
The human severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 8b protein is distinct from its counterpart in animal SARS-CoV and down-regulates the expression of the envelope protein in infected cells.Virology. 2006 Oct 10;354(1):132-42. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.06.026. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16876844 Free PMC article.
-
SARS coronavirus accessory proteins.Virus Res. 2008 Apr;133(1):113-21. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.10.009. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 18045721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the accessory viral proteins unique to the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus.Antiviral Res. 2006 Nov;72(2):78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2006.05.010. Epub 2006 Jun 6. Antiviral Res. 2006. PMID: 16820226 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DisCoVering potential candidates of RNAi-based therapy for COVID-19 using computational methods.PeerJ. 2021 Feb 26;9:e10505. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10505. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33680575 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasome regulation in driving COVID-19 severity in humans and immune tolerance in bats.J Leukoc Biol. 2022 Feb;111(2):497-508. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4COVHR0221-093RR. Epub 2021 May 31. J Leukoc Biol. 2022. PMID: 34057760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-uniform aspects of the SARS-CoV-2 intraspecies evolution reopen question of its origin.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Dec 1;222(Pt A):972-993. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.09.184. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 36174872 Free PMC article.
-
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 non-structural proteins 1 and 15 proteins mediate antiviral immune evasion.Curr Res Virol Sci. 2022;3:100021. doi: 10.1016/j.crviro.2022.100021. Epub 2022 Feb 12. Curr Res Virol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35187506 Free PMC article.
-
Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected.Virology. 2009 Dec 5;395(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19800091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harper J.W., Adami G.R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S.J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993;75(4):805–816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

