Thymosin-alpha1 modulates dendritic cell differentiation and functional maturation from human peripheral blood CD14+ monocytes
- PMID: 17532057
- PMCID: PMC1986709
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imlet.2007.04.007
Thymosin-alpha1 modulates dendritic cell differentiation and functional maturation from human peripheral blood CD14+ monocytes
Abstract
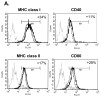
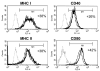
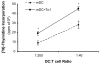
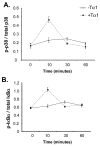
Although thymosins have been demonstrated to have immunomodulatory effects, it is still not clear whether they could affect dendritic cells (DCs), the most professional antigen-presenting cells. The objective of this study was to determine the effect and potential mechanisms of thymosin-alpha1 (Talpha1) on DC differentiation and functional maturation. Human peripheral blood CD14(+) monocytes were purified by using a magnetic separation column and cultured with GM-CSF and IL-4 to differentiate into immature DCs (iDCs). In the presence of Talpha1, iDC surface markers CD40, CD80, MHC class I and class II molecules were significantly upregulated as measured by flow cytemotry analysis. However, Tbeta4 or Tbeta10 did not show these effects on iDCs. There was an approximately 30% reduction in antigen (FITC-conjugated dextran)-uptake by Talpha1-treated iDCs as compared with non-Talpha1-treated iDCs. In addition, Talpha1-treated matured DCs (mDCs) showed an increased stimulation of allogeneic CD3(+) T-cell proliferation as measured by a mixed-lymphocyte reaction assay. Talpha1-treated mDCs also increased the production of several Th1- and Th2-type cytokines as measured by a Bio-Plex cytokine assay. Furthermore, rapid activation of p38 MAPK and NFkappaB was seen in Talpha1-treated iDCs as measured by a Bio-Plex phosphoprotein assay. Thus, Talpha1 significantly enhances DC differentiation, activation, and functions from human peripheral blood CD14(+) monocytes possibly through a mechanism of the activation of p38 MAPK and NFkappaB pathways. This study provides a basis to further evaluate Talpha1 as a possible adjuvant for a DC-directed vaccine or therapy.
Figures


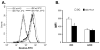
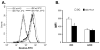
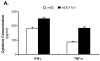
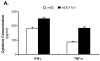
Similar articles
-
1-alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)(2)D(3)) hampers the maturation of fully active immature dendritic cells from monocytes.Eur J Endocrinol. 2001 Sep;145(3):351-7. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1450351. Eur J Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11517017
-
The modulation of thymosin alpha 1 in the maturation, differentiation and function of murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells in the absence or presence of tumor necrosis factor-alpha.Int Immunopharmacol. 2004 Apr;4(4):539-46. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2004.02.008. Int Immunopharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15099531
-
Human Chorionic Villous Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modify the Functions of Human Dendritic Cells, and Induce an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype in CD1+ Dendritic Cells.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015 Jun;11(3):423-41. doi: 10.1007/s12015-014-9562-8. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015. PMID: 25287760
-
Dual effect of Thymosin α 1 on human monocyte-derived dendritic cell in vitro stimulated with viral and bacterial toll-like receptor agonists.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15 Suppl 1:S59-70. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2015.1019460. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26096650
-
Preclinical studies with IRX-2 and thymosin alpha1 in combination therapy.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Apr;1194:162-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05475.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20536465 Review.
Cited by
-
Thymosin α1 therapy in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A multicenter retrospective cohort study.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Nov;88:106873. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106873. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32795897 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical practice of sepsis-induced immunosuppression: Current immunotherapy and future options.Chin J Traumatol. 2024 Mar;27(2):63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2023.11.001. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Chin J Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 38040590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tetanus toxoid-pulsed monocyte vaccination for augmentation of collateral vessel growth.J Am Heart Assoc. 2014 Apr 14;3(2):e000611. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000611. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014. PMID: 24732919 Free PMC article.
-
Thymosin α1 protects from CTLA-4 intestinal immunopathology.Life Sci Alliance. 2020 Aug 14;3(10):e202000662. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202000662. Print 2020 Oct. Life Sci Alliance. 2020. PMID: 32817121 Free PMC article.
-
CTLA-4 Blockade, during HIV Virus-Like Particles Immunization, Alters HIV-Specific B-Cell Responses.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Jun 6;8(2):284. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8020284. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32517277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manca F, Li Pira G, Fenoglio D, Fang SP, Habeshaw A, Knight SC, et al. Dendritic cells are potent antigen-presenting cells for in vitro induction of primary human CD4+ T-cell lines specific for HIV gp120. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1994;7:15–23. - PubMed
-
- Shortman K, Liu YJ. Mouse and human dendritic cell subtypes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:151–61. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, Steinman RM. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 1998;392:245–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

