Up-regulation of IL-6 and TNF-alpha induced by SARS-coronavirus spike protein in murine macrophages via NF-kappaB pathway
- PMID: 17532082
- PMCID: PMC7114322
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.02.007
Up-regulation of IL-6 and TNF-alpha induced by SARS-coronavirus spike protein in murine macrophages via NF-kappaB pathway
Abstract
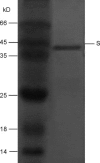
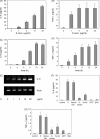
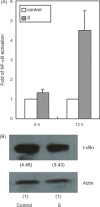
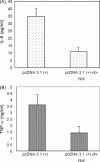
The clinical picture of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is characterized by an over-exuberant immune response with lung lymphomononuclear cells infilteration and proliferation that may account for tissue damage more than the direct effect of viral replication. To understand how cells response in the early stage of virus-host cell interaction, in this study, a purified recombinant S protein was studied for stimulating murine macrophages (RAW264.7) to produce proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-alpha) and chemokine IL-8. We found that direct induction of IL-6 and TNF-alpha release in the supernatant in a dose-, time-dependent manner and highly spike protein-specific, but no induction of IL-8 was detected. Further experiments showed that IL-6 and TNF-alpha production were dependent on NF-kappaB, which was activated through I-kappaBalpha degradation. These results suggest that SARS-CoV spike protein may play an important role in the pathogenesis of SARS, especially in inflammation and high fever.
Figures
References
-
- Chang Y.J., Liu C.Y., Chiang B.L., Chao Y.C., Chen C.C. Induction of IL-8 release in lung cells via activator protein-1 by recombinant baculovirus displaying severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus spike proteins: identification of two functional regions. J. Immunol. 2004;173(12):7602–7614. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z., Zhang L., Qin C., Ba L., Yi C.E., Zhang F., Wei Q., He T., Yu W., Yu J., Gao H., Tu X., Gettie A., Farzan M., Yuen K.Y., Ho D.D. Recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara expressing the spike glycoprotein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus induces protective neutralizing antibodies primarily targeting the receptor binding region. J. Virol. 2005;79(5):2678–2688. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

