Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of (-)-beta-D-(2R,4R)-1,3-dioxolane-2,6-diamino purine (DAPD) (amdoxovir) and (-)-beta-D-(2R,4R)-1,3-dioxolane guanosine (DXG) prodrugs
- PMID: 17532483
- PMCID: PMC2025703
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2007.03.005
Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of (-)-beta-D-(2R,4R)-1,3-dioxolane-2,6-diamino purine (DAPD) (amdoxovir) and (-)-beta-D-(2R,4R)-1,3-dioxolane guanosine (DXG) prodrugs
Abstract
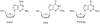
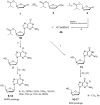
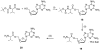
Prodrugs of (-)-beta-D-(2R,4R)-1,3-dioxolane-2,6-diamino purine (DAPD), organic salts of DAPD, 5'-L-valyl DAPD and N-1 substituted (-)-beta-D-(2R,4R)-1,3-dioxolane guanosine (DXG) have been synthesized with the objective of finding molecules which might be superior to DAPD and DXG in solubility as well as pharmacologic profiles. Synthesized prodrugs were evaluated for anti-HIV activity against HIV-1(LAI) in primary human lymphocytes (PBM cells) as well as their cytotoxicity in PBM, CEM and Vero cells. DAPD prodrugs, modified at the C6 position of the purine ring, demonstrated several folds of enhanced anti-HIV activity in comparison to the parent compound DAPD without increasing the toxicity. The presence of alkyl amino groups at the C6 position of the purine ring increased the antiviral potency several folds, and the most potent compound (-)-beta-D-(2R,4R)-1,3-dioxolane-2-amino-6-aminoethyl purine (8) was 17 times more potent than that of DAPD. 5'-L-Valyl DAPD 20 and organic acid salts 21-24 also exhibited enhanced anti-HIV activity in comparison to DAPD, while DXG prodrugs 16 and 17 exhibited lower potency than that of DXG or DAPD.
Figures
References
-
- Badet B, Julia M, Lefebvre C. The efficiency of diphenylsulfonium salts as alkylating agents. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1984;11:431–434.
-
- Baer HP, Drummond GI, Gillis J. Studies on the specificity and mechanism of action of adenosine deaminase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968;123:172–178. - PubMed
-
- Balzarini J. Metabolism and mechanism of antiviral action of purine and pyrimidine derivatives. Pharm. World Sci. 1994;16:113–126. - PubMed
-
- Barchi JJ, Marquez VE, Driscoll JS, Ford H, Mitsuya H, Shirasaka T, Aoki S, Kelley JA. Potential anti-AIDS drugs. lipophilic, adenosine deaminase-activated prodrugs. J. Med. Chem. 1991;34:1647–1655. - PubMed
-
- Bazmi HZ, Hammond JL, Cavalcanti SCH, Chu CK, Schinazi RF, Mellors JW. In vitro selection of mutations in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase that decrease susceptibility to (-)-β-D-dioxolane-guanosine and suppress resistance to 3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000;44:1783–1788. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

