Defining SH2 domain and PTP specificity by screening combinatorial peptide libraries
- PMID: 17532507
- PMCID: PMC2041848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.02.010
Defining SH2 domain and PTP specificity by screening combinatorial peptide libraries
Abstract
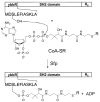
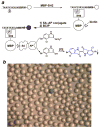
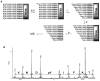
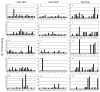
Src homology 2 (SH2) domains mediate protein-protein interactions by recognizing short phosphotyrosyl (pY) peptide motifs in their partner proteins. Protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) catalyze the dephosphorylation of pY proteins, counteracting the protein tyrosine kinases. Both types of proteins exhibit primary sequence specificity, which plays at least a partial role in dictating their physiological interacting partners or substrates. A combinatorial peptide library method has been developed to systematically assess the sequence specificity of SH2 domains and PTPs. A "one-bead-one-compound" pY peptide library is synthesized on 90-microm TentaGel beads and screened against an SH2 domain or PTP of interest for binding or catalysis. The beads that carry the tightest binding sequences against the SH2 domain or the most efficient substrates of the PTP are selected by an enzyme-linked assay and individually sequenced by a partial Edman degradation/mass spectrometry technique. The combinatorial method has been applied to determine the sequence specificity of 8 SH2 domains from Src and Csk kinases, adaptor protein Grb2, and phosphatases SHP-1, SHP-2, and SHIP1 and a prototypical PTP, PTP1B.
Figures


References
-
- Venter JC, et al. Science. 2001;291:1304–1351. - PubMed
-
- Waksman G, Kominos D, Robertson SC, Pant N, Baltimore D, Birge RB, Cowburn D, Hanafusa H, Mayer BJ, Overduin M, Resh MD, Rios CB, Silverman L, Kuriyan J. Nature. 1992;358:646–653. - PubMed
-
- Blaikie P, Immanuel D, Wu J, Li N, Yajnik V. B Margolis J Biol Chem. 1994;269:32031–3203. - PubMed
-
- Songyang Z, Shoelson SE, Chaudhuri M, Gish G, Pawson T, Haser WG, King F, Roberts T, Ratnofsky S, Lechleider RJ, Neel BG, Birge RB, Fajardo JE, Chou MM, Hanafusa H, Schaffhausen B. L C Cantley Cell. 1993;72:767–778. - PubMed
-
- Burshtyn DN, Yang W, Yi T, Long EO. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:13066–13072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

