An immunohistochemical study of the triangular fibrocartilage complex of the wrist: regional variations in cartilage phenotype
- PMID: 17532798
- PMCID: PMC2375804
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00742.x
An immunohistochemical study of the triangular fibrocartilage complex of the wrist: regional variations in cartilage phenotype
Abstract
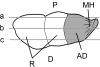
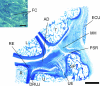
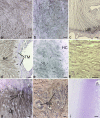
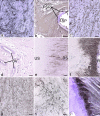
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) transmits load from the wrist to the ulna and stabilizes the distal radioulnar joint. Damage to it is a major cause of wrist pain. Although its basic structure is well established, little is known of its molecular composition. We have analysed the immunohistochemical labelling pattern of the extracellular matrix of the articular disc and the meniscal homologue of the TFCC in nine elderly individuals (age range 69-96 years), using a panel of monoclonal antibodies directed against collagens, glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans and cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP). Although many of the molecules (types I, III and VI collagen, chondroitin 4 sulphate, dermatan sulphate and keratan sulphate, the oversulphated epitope of chondroitin 6 sulphate, versican and COMP) were found in all parts of the TFCC, aggrecan, link protein and type II collagen were restricted to the articular disc and to entheses. They were thus not a feature of the meniscal homologue. The shift in tissue phenotype within the TFCC, from a fibrocartilaginous articular disc to a more fibrous meniscal homologue, correlates with biomechanical data suggesting that the radial region is stiff and subject to considerable stress concentration. The presence of aggrecan, link protein and type II collagen in the articular disc could explain why the TFCC is destroyed in rheumatoid arthritis, given that it has been suggested that autoimmunity to these antigens results in the destruction of articular cartilage. The differential distribution of aggrecan within the TFCC is likely to be reflected by regional differences in water content and mobility on the radial and ulnar side. This needs to be taken into account in the design of improved MRI protocols for visualizing this ulnocarpal complex of the wrist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An immunohistochemical study of the extracellular matrix of the tarsal plate in the upper eyelid in human beings.J Anat. 2005 Jan;206(1):37-45. doi: 10.1111/j.0021-8782.2005.00363.x. J Anat. 2005. PMID: 15679869 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular parameters indicating adaptation to mechanical stress in fibrous connective tissue.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2005;178:1-71. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16080262 Review.
-
Fibrocartilage in the transverse ligament of the human acetabulum.J Anat. 2001 Feb;198(Pt 2):223-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2001.19820223.x. J Anat. 2001. PMID: 11273046 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrocartilage at the entheses of the suprascapular (superior transverse scapular) ligament of man--a ligament spanning two regions of a single bone.J Anat. 2001 Nov;199(Pt 5):539-45. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2001.19950539.x. J Anat. 2001. PMID: 11760885 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of combined arthroscopic triangular fibrocartilage complex debridement and arthroscopic wafer distal ulna resection versus arthroscopic triangular fibrocartilage complex debridement and ulnar shortening osteotomy for ulnocarpal abutment syndrome.Arthroscopy. 2004 Apr;20(4):392-401. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2004.01.013. Arthroscopy. 2004. PMID: 15067279 Review.
Cited by
-
Elastic fiber-mediated enthesis in the human middle ear.J Anat. 2012 Oct;221(4):331-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2012.01542.x. Epub 2012 Jul 16. J Anat. 2012. PMID: 22803514 Free PMC article.
-
An immunohistochemical study of the extracellular matrix of entheses associated with the human pisiform bone.J Anat. 2008 May;212(5):645-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2008.00887.x. Epub 2008 Apr 8. J Anat. 2008. PMID: 18399959 Free PMC article.
-
Letter to the editor: how does ulnar shortening osteotomy influence morphologic changes in the triangular fibrocartilage complex?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Jan;473(1):397-8. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-4041-8. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 25373937 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Degeneration of the articular disc in the human triangular fibrocartilage complex.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021 Apr;141(4):699-708. doi: 10.1007/s00402-021-03795-2. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021. PMID: 33550482
-
Ulnar Wrist Pain Revisited: Ultrasound Diagnosis and Guided Injection for Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injuries.J Clin Med. 2019 Sep 25;8(10):1540. doi: 10.3390/jcm8101540. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31557886 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams BD, Samani JE, Holley KA. Triangular fibrocartilage injury: a laboratory model. J Hand Surg. 1996;21A:189–193. - PubMed
-
- Asher RA, Perides G, Vanderhaeghen JJ, Bignami A. Extracellular matrix of central nervous system white matter: demonstration of an hyaluronate–protein complex. J Neurosci Res. 1991;28:410–421. - PubMed
-
- Asher RA, Scheibe RJ, Keiser HD, Bignami A. On the existence of a cartilage-like proteoglycan and link proteins in the central nervous system. Glia. 1995;13:294–308. - PubMed
-
- Bednar MS, Arnoczky SP, Weiland AJ. The microvasculature of the triangular fibrocartilage complex: its clinical significance. J Hand Surg. 1991;16A:1101–1105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

