Nonlinear optical imaging to evaluate the impact of obesity on mammary gland and tumor stroma
- PMID: 17532886
- PMCID: PMC2653856
Nonlinear optical imaging to evaluate the impact of obesity on mammary gland and tumor stroma
Abstract
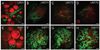
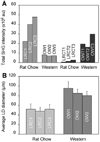
Obesity is an established risk factor for breast cancer incidence and mortality. However, the mechanism that links obesity to tumorigenesis is not well understood. Here we combined nonlinear optical imaging technologies with an early-onset diet-induced obesity breast cancer animal model to evaluate the impact of obesity on the composition of mammary gland and tumor stroma. Using coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering and second harmonic generation on the same platform, we simultaneously imaged mammary adipocytes, blood capillaries, collagen fibrils, and tumor cells without any labeling. We observed that obesity increases the size of lipid droplets of adipocytes in mammary gland and collagen content in mammary tumor stroma, respectively. Such impacts of obesity on mammary gland and tumor stroma could not be analyzed using standard two-dimensional histologic evaluation. Given the importance of mammary stroma to the growth and migration of tumor cells, our observation provides the first imaging evidence that supports the relationship between obesity and breast cancer risk.
Figures


References
-
- Marx J. Unraveling the causes of diabetes. Science. 2002;296:686–689. - PubMed
-
- Lorincz AM, Sukumar S. Molecular links between obesity and breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006;13:279–292. - PubMed
-
- Barnett JB. The relationship between obesity and breast cancer risk and mortality. Nutr Rev. 2003;61:73–76. - PubMed
-
- Narod S, Lynch H, Conway T, et al. Increasing incidence of breast-cancer infamily with Brcal mutation. Lancet. 1993;341:1101–1102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
