Short RNA guides cleavage by eukaryotic RNase III
- PMID: 17534422
- PMCID: PMC1868780
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000472
Short RNA guides cleavage by eukaryotic RNase III
Abstract
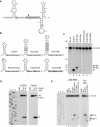
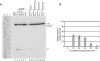
In eukaryotes, short RNAs guide a variety of enzymatic activities that range from RNA editing to translation repression. It is hypothesized that pre-existing proteins evolved to bind and use guide RNA during evolution. However, the capacity of modern proteins to adopt new RNA guides has never been demonstrated. Here we show that Rnt1p, the yeast orthologue of the bacterial dsRNA-specific RNase III, can bind short RNA transcripts and use them as guides for sequence-specific cleavage. Target cleavage occurred at a constant distance from the Rnt1p binding site, leaving the guide RNA intact for subsequent cleavage. Our results indicate that RNase III may trigger sequence-specific RNA degradation independent of the RNAi machinery, and they open the road for a new generation of precise RNA silencing tools that do not trigger a dsRNA-mediated immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular requirements for duplex recognition and cleavage by eukaryotic RNase III: discovery of an RNA-dependent DNA cleavage activity of yeast Rnt1p.J Mol Biol. 2004 Apr 23;338(2):401-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.02.059. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15066440
-
Structure and function of Rnt1p: An alternative to RNAi for targeted RNA degradation.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019 May;10(3):e1521. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1521. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019. PMID: 30548404 Review.
-
Sequence dependence of substrate recognition and cleavage by yeast RNase III.J Mol Biol. 2003 Apr 11;327(5):985-1000. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00231-6. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12662924
-
Recognition of a conserved class of RNA tetraloops by Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNase III.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Mar 28;97(7):3142-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.7.3142. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10716739 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for non-catalytic and catalytic activities of ribonuclease III.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006 Aug;62(Pt 8):933-40. doi: 10.1107/S090744490601153X. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006. PMID: 16855311 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of a ribonuclease III-like protein required for cleavage of the pre-rRNA in the 3'ETS in Arabidopsis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Mar;36(4):1163-75. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm1130. Epub 2007 Dec 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18158302 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome wide annotation of eukaryotic RNase III reactivity and degradation signals.PLoS Genet. 2015 Feb 13;11(2):e1005000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005000. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25680180 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic RNA modules for fine-tuning gene expression levels in yeast by modulating RNase III activity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Oct;39(19):8651-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr445. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21737428 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of a eukaryotic RNase III postcleavage complex reveals a double-ruler mechanism for substrate selection.Mol Cell. 2014 May 8;54(3):431-44. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.006. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Mol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24703949 Free PMC article.
-
RNA editing in Trypanosoma brucei requires three different editosomes.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jan;28(1):122-30. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01374-07. Epub 2007 Oct 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 17954557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tijsterman M, Plasterk RH. Dicers at RISC; the mechanism of RNAi. Cell. 2004;117:1–3. - PubMed
-
- Xia H, Mao Q, Paulson HL, Davidson BL. siRNA-mediated gene silencing in vitro and in vivo. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:1006–1010. - PubMed
-
- Lamontagne B, Larose S, Boulanger J, Elela SA. The RNase III family: a conserved structure and expanding functions in eukaryotic dsRNA metabolism. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2001;3:71–78. - PubMed
-
- Ge D, Lamontagne B, Elela SA. RNase III-Mediated Silencing of a Glucose-Dependent Repressor in Yeast. Curr Biol. 2005;15:140–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

