Prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of human monoclonal antibodies against H5N1 influenza
- PMID: 17535101
- PMCID: PMC1880850
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040178
Prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of human monoclonal antibodies against H5N1 influenza
Abstract
Background: New prophylactic and therapeutic strategies to combat human infections with highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N1 viruses are needed. We generated neutralizing anti-H5N1 human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and tested their efficacy for prophylaxis and therapy in a murine model of infection.
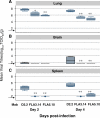
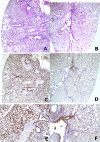
Methods and findings: Using Epstein-Barr virus we immortalized memory B cells from Vietnamese adults who had recovered from infections with HPAI H5N1 viruses. Supernatants from B cell lines were screened in a virus neutralization assay. B cell lines secreting neutralizing antibodies were cloned and the mAbs purified. The cross-reactivity of these antibodies for different strains of H5N1 was tested in vitro by neutralization assays, and their prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy in vivo was tested in mice. In vitro, mAbs FLA3.14 and FLD20.19 neutralized both Clade I and Clade II H5N1 viruses, whilst FLA5.10 and FLD21.140 neutralized Clade I viruses only. In vivo, FLA3.14 and FLA5.10 conferred protection from lethality in mice challenged with A/Vietnam/1203/04 (H5N1) in a dose-dependent manner. mAb prophylaxis provided a statistically significant reduction in pulmonary virus titer, reduced associated inflammation in the lungs, and restricted extrapulmonary dissemination of the virus. Therapeutic doses of FLA3.14, FLA5.10, FLD20.19, and FLD21.140 provided robust protection from lethality at least up to 72 h postinfection with A/Vietnam/1203/04 (H5N1). mAbs FLA3.14, FLD21.140 and FLD20.19, but not FLA5.10, were also therapeutically active in vivo against the Clade II virus A/Indonesia/5/2005 (H5N1).
Conclusions: These studies provide proof of concept that fully human mAbs with neutralizing activity can be rapidly generated from the peripheral blood of convalescent patients and that these mAbs are effective for the prevention and treatment of H5N1 infection in a mouse model. A panel of neutralizing, cross-reactive mAbs might be useful for prophylaxis or adjunctive treatment of human cases of H5N1 influenza.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- No Authors Listed. Epidemiology of WHO-confirmed human cases of avian influenza A(H5N1) infection. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2006;81:249–257. - PubMed
-
- Li KS, Guan Y, Wang J, Smith GJ, Xu KM, et al. Genesis of a highly pathogenic and potentially pandemic H5N1 influenza virus in eastern Asia. Nature. 2004;430:209–213. - PubMed
-
- Puthavathana P, Auewarakul P, Charoenying PC, Sangsiriwut K, Pooruk P, et al. Molecular characterization of the complete genome of human influenza H5N1 virus isolates from Thailand. J Gen Virol. 2005;86:423–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

