Regulation of p73 by Hck through kinase-dependent and independent mechanisms
- PMID: 17535448
- PMCID: PMC1899183
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-45
Regulation of p73 by Hck through kinase-dependent and independent mechanisms
Abstract
Background: p73, a p53 family member is a transcription factor that plays a role in cell cycle, differentiation and apoptosis. p73 is regulated through post translational modifications and protein interactions. c-Abl is the only known tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates and activates p73. Here we have analyzed the role of Src family kinases, which are involved in diverse signaling pathways, in regulating p73.
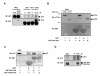
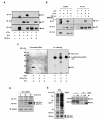
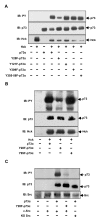
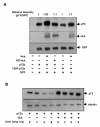
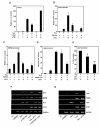
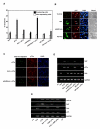
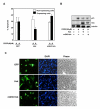
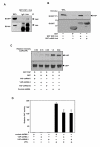
Results: Exogenously expressed as well as cellular Hck and p73 interact in vivo. In vitro binding assays show that SH3 domain of Hck interacts with p73. Co-expression of p73 with Hck or c-Src in mammalian cells resulted in tyrosine phosphorylation of p73. Using site directed mutational analysis, we determined that Tyr-28 was the major site of phosphorylation by Hck and c-Src, unlike c-Abl which phosphorylates Tyr-99. In a kinase dependent manner, Hck co-expression resulted in stabilization of p73 protein in the cytoplasm. Activation of Hck in HL-60 cells resulted in tyrosine phosphorylation of endogenous p73. Both exogenous and endogenous Hck localize to the nuclear as well as cytoplasmic compartment, just as does p73. Ectopically expressed Hck repressed the transcriptional activity of p73 as determined by promoter assays and semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the p73 target, Ipaf and MDM2. SH3 domain- dependent function of Hck was required for its effect on p73 activity, which was also reflected in its ability to inhibit p73-mediated apoptosis. We also show that Hck interacts with Yes associated protein (YAP), a transcriptional co-activator of p73, and shRNA mediated knockdown of YAP protein reduces p73 induced Ipaf promoter activation.
Conclusion: We have identified p73 as a novel substrate and interacting partner of Hck and show that it regulates p73 through mechanisms that are dependent on either catalytic activity or protein interaction domains. Hck-SH3 domain-mediated interactions play an important role in the inhibition of p73-dependent transcriptional activation of a target gene, Ipaf, as well as apoptosis.
Figures

References
-
- Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, Creancier L, Biscan JC, Valent A, Minty A, Chalon P, Lelias JM, Dumont X, et al. Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell. 1997;90:809–819. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80540-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

