Alarin is a vasoactive peptide
- PMID: 17535903
- PMCID: PMC1891251
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0608585104
Alarin is a vasoactive peptide
Abstract
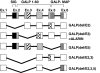
Galanin-like peptide (GALP) is a hypothalamic neuropeptide belonging to the galanin family of peptides. The GALP gene is characterized by extensive differential splicing in a variety of murine tissues. One splice variant excludes exon 3 and results in a frame shift leading to a novel peptide sequence and a stop codon after 49 aa. In this peptide, which we termed alarin, the signal sequence of the GALP precursor peptide and the first 5 aa of the mature GALP are followed by 20 aa without homology to any other murine protein. Alarin mRNA was detected in murine brain, thymus, and skin. In accordance with its vascular localization, the peptide exhibited potent and dose-dependent vasoconstrictor and anti-edema activity in the cutaneous microvasculature, as was also observed with other members of the galanin peptide family. However, in contrast to galanin peptides in general, the physiological effects of alarin do not appear to be mediated via the known galanin receptors. Alarin adds another facet to the surprisingly high-functional redundancy of the galanin family of peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
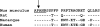




References
-
- Hoyle CH. Brain Res. 1999;848:1–25. - PubMed
-
- Tatemoto K, Rokaeus A, Jornvall H, McDonald TJ, Mutt V. FEBS Lett. 1983;164:124–128. - PubMed
-
- Ohtaki T, Kumano S, Ishibashi Y, Ogi K, Matsui H, Harada M, Kitada C, Kurokawa T, Onda H, Fujino M. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:37041–37045. - PubMed
-
- Krasnow SM, Fraley GS, Schuh SM, Baumgartner JW, Clifton DK, Steiner RA. Endocrinology. 2003;144:813–822. - PubMed
-
- Gottsch ML, Clifton DK, Steiner RA. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004;15:215–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

