NPM/ALK binds and phosphorylates the RNA/DNA-binding protein PSF in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 17537995
- PMCID: PMC1988934
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-01-028647
NPM/ALK binds and phosphorylates the RNA/DNA-binding protein PSF in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
Abstract
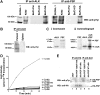
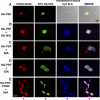
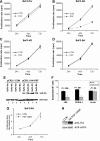
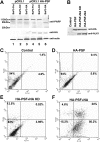
The oncogenic fusion tyrosine kinase nucleophosmin/anaplastic lymphoma kinase (NPM/ALK) induces cellular transformation in anaplastic large-cell lymphomas (ALCLs) carrying the t(2;5) chromosomal translocation. Protein-protein interactions involving NPM/ALK are important for the activation of downstream signaling pathways. This study was aimed at identifying novel NPM/ALK-binding proteins that might contribute to its oncogenic transformation. Using a proteomic approach, several RNA/DNA-binding proteins were found to coimmunoprecipitate with NPM/ALK, including the multifunctional polypyrimidine tract binding proteinassociated splicing factor (PSF). The interaction between NPM/ALK and PSF was dependent on an active ALK kinase domain and PSF was found to be tyrosine-phosphorylated in NPM/ALK-expressing cell lines and in primary ALK(+) ALCL samples. Furthermore, PSF was shown to be a direct substrate of purified ALK kinase domain in vitro, and PSF Tyr293 was identified as the site of phosphorylation. Y293F PSF was not phosphorylated by NPM/ALK and was not delocalized in NPM/ALK(+) cells. The expression of ALK fusion proteins induced delocalization of PSF from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and forced overexpression of PSF-inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in cells expressing NPM/ALK. PSF phosphorylation also increased its binding to RNA and decreased the PSF-mediated suppression of GAGE6 expression. These results identify PSF as a novel NPM/ALK-binding protein and substrate, and suggest that PSF function may be perturbed in NPM/ALK-transformed cells.
Figures
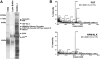
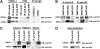
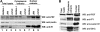
References
-
- Stein H, Foss HD, Durkop H, et al. CD30(+) anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a review of its histopathologic, genetic, and clinical features. Blood. 2000;96:3681–3695. - PubMed
-
- Morris SW, Xue L, Ma Z, Kinney MC. Alk+ CD30+ lymphomas: a distinct molecular genetic subtype of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2001;113:275–295. - PubMed
-
- Morris SW, Naeve C, Mathew P, et al. ALK, the chromosome 2 gene locus altered by the t(2;5) in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, encodes a novel neural receptor tyrosine kinase that is highly related to leukocyte tyrosine kinase (LTK). Oncogene. 1997;14:2175–2188. - PubMed
-
- Iwahara T, Fujimoto J, Wen D, et al. Molecular characterization of ALK, a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed specifically in the nervous system. Oncogene. 1997;14:439–449. - PubMed
-
- Pulford K, Morris SW, Turturro F. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase proteins in growth control and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2004;199:330–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

