Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis
- PMID: 17540599
- PMCID: PMC1939978
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.05.010
Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis
Abstract
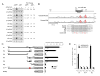
The p53 tumor suppressor protein is a critical regulator of the cellular response to cancer-initiating insults such as genotoxic stress. In this report, we demonstrate that microRNAs (miRNAs) are important components of the p53 transcriptional network. Global miRNA expression analyses identified a cohort of miRNAs that exhibit p53-dependent upregulation following DNA damage. One such miRNA, miR-34a, is commonly deleted in human cancers and, as shown here, frequently absent in pancreatic cancer cells. Characterization of the miR-34a primary transcript and promoter demonstrates that this miRNA is directly transactivated by p53. Expression of miR-34a causes dramatic reprogramming of gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Much like the known set of p53-regulated genes, miR-34a-responsive genes are highly enriched for those that regulate cell-cycle progression, apoptosis, DNA repair, and angiogenesis. Therefore, it is likely that an important function of miR-34a is the modulation and fine-tuning of the gene expression program initiated by p53.
Figures
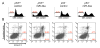

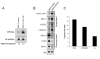
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Bagchi A, Papazoglu C, Wu Y, Capurso D, Brodt M, Francis D, Bredel M, Vogel H, Mills AA. CHD5 Is a Tumor Suppressor at Human 1p36. Cell. 2007;128:459–475. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Bello MJ, Leone PE, Vaquero J, de Campos JM, Kusak ME, Sarasa JL, Pestana A, Rey JA. Allelic loss at 1p and 19q frequently occurs in association and may represent early oncogenic events in oligodendroglial tumors. Int J Cancer. 1995;64:207–210. - PubMed
-
- Bieche I, Champeme MH, Matifas F, Cropp CS, Callahan R, Lidereau R. Two distinct regions involved in 1p deletion in human primary breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1993;53:1990–1994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

