Increased tumor cell dissemination and cellular senescence in the absence of beta1-integrin function
- PMID: 17541405
- PMCID: PMC1894776
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601738
Increased tumor cell dissemination and cellular senescence in the absence of beta1-integrin function
Abstract
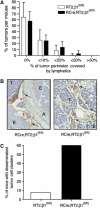
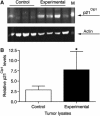
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that bind extracellular matrix proteins and enable cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization, as well as transduction of signals into cells, to promote various aspects of cellular behavior, such as proliferation or survival. Integrins participate in many aspects of tumor biology. Here, we have employed the Rip1Tag2 transgenic mouse model of pancreatic beta cell carcinogenesis to investigate the role of beta(1)-integrin in tumor progression. Specific ablation of beta(1)-integrin function in pancreatic beta cells resulted in a defect in sorting between insulin-expressing beta cells and glucagon-expressing alpha cells in islets of Langerhans. Ablation of beta(1)-integrin in beta tumor cells of Rip1Tag2 mice led to the dissemination of tumor cell emboli into lymphatic blood vessels in the absence of ongoing lymphangiogenesis. Yet, disseminating beta(1)-integrin-deficient beta tumor cells did not elicit metastasis. Rather, primary tumor growth was significantly impaired by reduced tumor cell proliferation and the acquisition of cellular senescence by beta(1)-integrin-deficient beta tumor cells. The results indicate a critical role of beta(1)-integrin function in mediating metastatic dissemination and preventing tumor cell senescence.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Distinct roles of beta1 integrins during angiogenesis.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;85(3-4):243-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2005.09.010. Epub 2005 Oct 10. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16546568 Review.
-
Reduced expression of neural cell adhesion molecule induces metastatic dissemination of pancreatic beta tumor cells.Nat Med. 1999 Mar;5(3):286-91. doi: 10.1038/6502. Nat Med. 1999. PMID: 10086383
-
Expression and cellular distribution of alpha(v)integrins in beta(1)integrin-deficient embryonic stem cell-derived cardiac cells.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001 Mar;33(3):521-32. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.2000.1326. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001. PMID: 11181020
-
A bioluminescent mouse model of pancreatic {beta}-cell carcinogenesis.Carcinogenesis. 2010 Aug;31(8):1465-74. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq109. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20530553
-
The role of beta 1 integrins in tumors.Semin Cancer Biol. 1993 Oct;4(5):277-83. Semin Cancer Biol. 1993. PMID: 7504957 Review.
Cited by
-
Beta 1 integrin signaling mediates pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma resistance to MEK inhibition.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 7;10(1):11133. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67814-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32636409 Free PMC article.
-
Role of p38 MAP kinase in cancer stem cells and metastasis.Oncogene. 2022 Jun;41(23):3177-3185. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02329-3. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35501462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Extracellular Matrix: An Accomplice in Gastric Cancer Development and Progression.Cells. 2020 Feb 8;9(2):394. doi: 10.3390/cells9020394. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32046329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor (uPAR) Cooperates with Mutated KRAS in Regulating Cellular Plasticity and Gemcitabine Response in Pancreatic Adenocarcinomas.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;15(5):1587. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051587. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900379 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-independent integrin β1 signaling supports lung adenocarcinoma development.JCI Insight. 2022 Aug 8;7(15):e154098. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.154098. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35763345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA (1994) Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 264: 569–571 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

