Targeting NF-kappaB pathway with an IKK2 inhibitor induces inhibition of multiple myeloma cell growth
- PMID: 17542984
- PMCID: PMC2494583
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06629.x
Targeting NF-kappaB pathway with an IKK2 inhibitor induces inhibition of multiple myeloma cell growth
Abstract
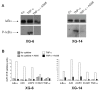
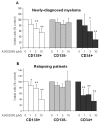
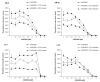
The pathophysiologic basis for multiple myeloma (MM) has been attributed to the dysregulation of various paracrine or autocrine growth factor loops and to perturbations in several signal transduction pathways including IkappaB kinase/nuclear factor-kappaB (IKK/NF-kappaB). The present study aimed at investigating the effect of a pharmaceutical IKK2 inhibitor, the anilinopyrimidine derivative AS602868, on the in vitro growth of 14 human MM cell lines (HMCL) and primary cells from 13 patients. AS602868 induced a clear dose-dependent inhibition of MM cell growth on both HMCL and primary MM cells, which was the result of a simultaneous induction of apoptosis and inhibition of the cell cycle progression. Combination of AS602868 with suboptimal doses of melphalan or Velcade showed an additive effect in growth inhibition of HMCL. AS602868 also induced apoptosis of primary myeloma cells. Importantly, AS602868 did not alter the survival of other bone marrow mononuclear cells (CD138(-)) co-cultured with primary MM (CD138(+)) cells, except for CD34(+) haematopoietic stem cells. The results demonstrate the important role of NF-kappaB in maintaining the survival of MM cells and suggest that a pharmacological inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway by the IKK2 inhibitor AS602868 can efficiently kill HMCL and primary myeloma cells and therefore might represent an innovative approach for treating MM patients.
Figures
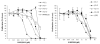
Similar articles
-
Canonical nuclear factor kappaB pathway inhibition blocks myeloma cell growth and induces apoptosis in strong synergy with TRAIL.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Oct 15;13(20):6010-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0140. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17947462
-
Inhibition of IkappaB kinase subunit 2 in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma down-regulates nuclear factor-kappaB constitutive activation, induces cell death, and potentiates the apoptotic response to antineoplastic chemotherapeutic agents.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Feb 1;14(3):901-11. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1419. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18245554
-
MLN120B, a novel IkappaB kinase beta inhibitor, blocks multiple myeloma cell growth in vitro and in vivo.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Oct 1;12(19):5887-94. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2501. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17020997
-
Can NF-kappaB be a target for novel and efficient anti-cancer agents?Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Oct 30;72(9):1054-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.07.023. Epub 2006 Sep 14. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16973133 Review.
-
The impact of NF-κB signaling on pathogenesis and current treatment strategies in multiple myeloma.Blood Rev. 2019 Mar;34:56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2018.11.003. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Blood Rev. 2019. PMID: 30501907 Review.
Cited by
-
TRAF6 is required for BLyS-mediated NF-κB signaling in multiple myeloma cells.Med Oncol. 2015 Oct;32(10):239. doi: 10.1007/s12032-015-0671-2. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Med Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26334396
-
Aberrant Activation of NF-κB Signalling in Aggressive Lymphoid Malignancies.Cells. 2018 Oct 30;7(11):189. doi: 10.3390/cells7110189. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30380749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-κB2 mutation targets survival, proliferation and differentiation pathways in the pathogenesis of plasma cell tumors.BMC Cancer. 2012 May 29;12:203. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-203. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22642622 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of canonical and noncanonical NF-κB pathways demonstrates significant antitumor activities in multiple myeloma.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Sep 1;18(17):4669-81. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0779. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22806876 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB and cancer-identifying targets and mechanisms.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008 Feb;18(1):19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2008.01.020. Epub 2008 Apr 24. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008. PMID: 18440219 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berenson JR, Ma HM, Vescio R. The role of nuclear factor-kappaB in the biology and treatment of multiple myeloma. Seminars in Oncology. 2001;28:626–633. - PubMed
-
- Bharti AC, Donato N, Singh S, Aggarwal BB. Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) down-regulates the constitutive activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and IkappaBalpha kinase in human multiple myeloma cells, leading to suppression of proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Blood. 2003;101:1053–1062. - PubMed
-
- Bharti AC, Shishodia S, Reuben JM, Weber D, Alexanian R, Raj-Vadhan S, Estrov Z, Talpaz M, Aggarwal BB. Nuclear factor-kappaB and STAT3 are constitutively active in CD138+ cells derived from multiple myeloma patients, and suppression of these transcription factors leads to apoptosis. Blood. 2004;103:3175–3184. - PubMed
-
- Brenne AT, Ro TB, Waage A, Sundan A, Borset M, Hjorth-Hansen H. Interleukin-21 is a growth and survival factor for human myeloma cells. Blood. 2002;99:3756–3762. - PubMed
-
- Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Moscinski L, Fernandez-Luna JL, Nunez G, Dalton WS, Jove R. Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity. 1999;10:105–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

