Glutamate receptor abnormalities in the YAC128 transgenic mouse model of Huntington's disease
- PMID: 17544587
- PMCID: PMC1995552
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.03.010
Glutamate receptor abnormalities in the YAC128 transgenic mouse model of Huntington's disease
Abstract
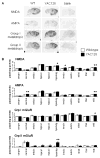
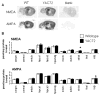
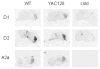
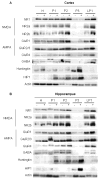
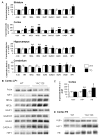
A yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) mouse model of Huntington's disease (YAC128) develops motor abnormalities, age-dependent striatal atrophy and neuronal loss. Alteration of neurotransmitter receptors, particularly glutamate and dopamine receptors, is a pathological hallmark of Huntington's disease. We therefore analyzed neurotransmitter receptors in symptomatic YAC128 Huntington's disease mice. We found significant increases in N-methyl-d-aspartate, AMPA and metabotropic glutamate receptor binding, which were not due to increases in receptor subunit mRNA expression levels. Subcellular fractionation analysis revealed increased levels of glutamate receptor subunits in synaptic membrane fractions from YAC128 mice. We found no changes in dopamine, GABA or adenosine receptor binding, nor did we see alterations in dopamine D1, D2 or adenosine A2a receptor mRNA levels. The receptor abnormalities in YAC128 transgenic mice thus appear limited to glutamate receptors. We also found a significant decrease in preproenkephalin mRNA in the striatum of YAC128 mice, which contrasts with the lack of change in levels of mRNA encoding neurotransmitter receptors. Taken together, the abnormal and selective increases in glutamate receptor subunit expression and binding are not due to increases in receptor subunit expression and may exert detrimental effects. The decrease in preproenkephalin mRNA suggests a selective transcriptional deficit, as opposed to neuronal loss, and could additionally contribute to the abnormal motor symptoms in YAC128 mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Albin RL, Greenamyre JT. Alternative excitotoxic hypotheses. Neurology. 1992;42:733–738. - PubMed
-
- Ariano MA, Aronin N, Difiglia M, Tagle DA, Sibley DR, Leavitt BR, Hayden MR, Levine MS. Striatal neurochemical changes in transgenic models of Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci Res. 2002;68:716–729. - PubMed
-
- Augood SJ, Faull RL, Love DR, Emson PC. Reduction in enkephalin and substance P messenger RNA in the striatum of early grade Huntington’s disease: a detailed cellular in situ hybridization study. Neuroscience. 1996;72:1023–1036. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF, Kowall NW, Ellison DW, Mazurek MF, Swartz KJ, Martin JB. Replication of the neurochemical characteristics of Huntington’s disease by quinolinic acid. Nature. 1986;321:168–171. - PubMed
-
- Benn CL, Farrell LA, Cha JH. Neurotransmitter receptor analysis in transgenic mouse models. Methods Mol Biol. 2004;277:231–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

