Activation and inhibition of photoreceptor guanylyl cyclase by guanylyl cyclase activating protein 1 (GCAP-1): the functional role of Mg2+/Ca2+ exchange in EF-hand domains
- PMID: 17545152
- PMCID: PMC2430010
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M702368200
Activation and inhibition of photoreceptor guanylyl cyclase by guanylyl cyclase activating protein 1 (GCAP-1): the functional role of Mg2+/Ca2+ exchange in EF-hand domains
Abstract
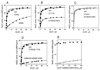
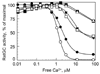
Guanylyl cyclase activating protein 1 (GCAP-1), a Ca(2+)/Mg(2+) sensor protein that accelerates retinal guanylyl cyclase (RetGC) in the light and decelerates it in the dark, is inactive in cation-free form. Binding of Mg(2+) in EF-hands 2 and 3 was essential for RetGC activation in the conditions mimicking light adaptation. Mg(2+) binding in EF-hand 2 affected the conformation of a neighboring non-metal binding domain, EF-hand-1, and increased GCAP-1 affinity for RetGC nearly 40-fold compared with the metal-free EF-hand 2. Mg(2+) binding in EF-hand 3 increased GCAP-1 affinity for RetGC 5-fold and its maximal RetGC stimulation 2-fold. Mg(2+) binding in EF-hand 4 affected neither GCAP-1 affinity for RetGC, nor RetGC activation. Inactivation of Ca(2+) binding in EF-hand 4 was sufficient to render GCAP-1 a constitutive activator of RetGC, whereas the EF-hand 3 role in Ca(2+)-dependent deceleration of RetGC was likely to be through the neighboring EF-hand 4. Inactivation of Ca(2+) binding in EF-hand 2 affected cooperativity of RetGC inhibition by Ca(2+), but did not prevent the inhibition. We conclude that 1) Mg(2+) binding in EF-hands 2 and 3, but not EF-hand 4, is essential for the ability of GCAP-1 to activate RetGC in the light; 2) Mg(2+) or Ca(2+) binding in EF-hand 3 and especially in EF-hand 2 is required for high-affinity interaction with the cyclase and affects the conformation of the neighboring EF-hand 1, a domain required for targeting RetGC; and 3) RetGC inhibition is likely to be primarily caused by Ca(2+) binding in EF-hand 4.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ca2+ and Mg2+ binding properties of GCAP-1. Evidence that Mg2+-bound form is the physiological activator of photoreceptor guanylyl cyclase.J Biol Chem. 2006 Aug 18;281(33):23830-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600257200. Epub 2006 Jun 22. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16793776
-
Guanylyl cyclase-activating proteins (GCAPs) are Ca2+/Mg2+ sensors: implications for photoreceptor guanylyl cyclase (RetGC) regulation in mammalian photoreceptors.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 23;279(17):16903-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C400065200. Epub 2004 Mar 1. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14993224
-
Factors that determine Ca2+ sensitivity of photoreceptor guanylyl cyclase. Kinetic analysis of the interaction between the Ca2+-bound and the Ca2+-free guanylyl cyclase activating proteins (GCAPs) and recombinant photoreceptor guanylyl cyclase 1 (RetGC-1).Biochemistry. 2004 Nov 2;43(43):13796-804. doi: 10.1021/bi048943m. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15504042
-
Mg2+/Ca2+ cation binding cycle of guanylyl cyclase activating proteins (GCAPs): role in regulation of photoreceptor guanylyl cyclase.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Jan;334(1-2):117-24. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0328-6. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19953307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of photoreceptor membrane guanylyl cyclases by guanylyl cyclase activator proteins.Methods. 1999 Dec;19(4):521-31. doi: 10.1006/meth.1999.0894. Methods. 1999. PMID: 10581151 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis of retinal membrane guanylate cyclase regulation by GCAP1 and RD3.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Sep 8;15:988142. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.988142. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36157073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of target binding site in photoreceptor guanylyl cyclase-activating protein 1 (GCAP1).J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 4;289(14):10140-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.540716. Epub 2014 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24567338 Free PMC article.
-
Differential calcium signaling by cone specific guanylate cyclase-activating proteins from the zebrafish retina.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023117. Epub 2011 Aug 2. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21829700 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of GCAP1 with retinal guanylyl cyclase and calcium: sensitivity to fatty acylation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 Feb 22;5:19. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00019. eCollection 2012. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22371697 Free PMC article.
-
Backbone (1)H, (13)C, and (15)N resonance assignments of guanylyl cyclase activating protein-1, GCAP1.Biomol NMR Assign. 2013 Apr;7(1):39-42. doi: 10.1007/s12104-012-9373-2. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Biomol NMR Assign. 2013. PMID: 22392341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pugh EN, Jr, Nikonov S, Lamb TD. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1999;9:410–418. - PubMed
-
- Arshavsky VY, Lamb TD, Pugh EN., Jr Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2002;64:153–187. - PubMed
-
- Olshevskaya EV, Ermilov AN, Dizhoor AM. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2002;230:139–147. - PubMed
-
- Burns ME, Baylor DA. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001;24:779–805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

