Infrequently transcribed long genes depend on the Set2/Rpd3S pathway for accurate transcription
- PMID: 17545470
- PMCID: PMC1877753
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1539307
Infrequently transcribed long genes depend on the Set2/Rpd3S pathway for accurate transcription
Abstract
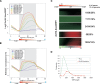
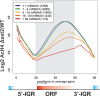
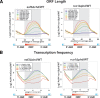
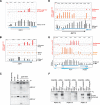
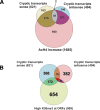
The presence of Set2-mediated methylation of H3K36 (K36me) correlates with transcription frequency throughout the yeast genome. K36me targets the Rpd3S complex to deacetylate transcribed regions and suppress cryptic transcription initiation at certain genes. Here, using a genome-wide approach, we report that the Set2-Rpd3S pathway is generally required for controlling acetylation at coding regions. When using acetylation as a functional readout for this pathway, we discovered that longer genes and, surprisingly, genes transcribed at lower frequency exhibit a stronger dependency. Moreover, a systematic screen using high-resolution tiling microarrays allowed us to identify a group of genes that rely on Set2-Rpd3S to suppress spurious transcripts. Interestingly, most of these genes are within the group that depend on the same pathway to maintain a hypoacetylated state at coding regions. These data highlight the importance of using the functional readout of histone codes to define the roles of specific pathways.
Figures
References
-
- Bannister A.J., Zegerman P., Partridge J.F., Miska E.A., Thomas J.O., Allshire R.C., Kouzarides T., Zegerman P., Partridge J.F., Miska E.A., Thomas J.O., Allshire R.C., Kouzarides T., Partridge J.F., Miska E.A., Thomas J.O., Allshire R.C., Kouzarides T., Miska E.A., Thomas J.O., Allshire R.C., Kouzarides T., Thomas J.O., Allshire R.C., Kouzarides T., Allshire R.C., Kouzarides T., Kouzarides T. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature. 2001;410:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Carrozza M.J., Li B., Florens L., Suganuma T., Swanson S.K., Lee K.K., Shia W.J., Anderson S., Yates J., Washburn M.P., Li B., Florens L., Suganuma T., Swanson S.K., Lee K.K., Shia W.J., Anderson S., Yates J., Washburn M.P., Florens L., Suganuma T., Swanson S.K., Lee K.K., Shia W.J., Anderson S., Yates J., Washburn M.P., Suganuma T., Swanson S.K., Lee K.K., Shia W.J., Anderson S., Yates J., Washburn M.P., Swanson S.K., Lee K.K., Shia W.J., Anderson S., Yates J., Washburn M.P., Lee K.K., Shia W.J., Anderson S., Yates J., Washburn M.P., Shia W.J., Anderson S., Yates J., Washburn M.P., Anderson S., Yates J., Washburn M.P., Yates J., Washburn M.P., Washburn M.P., et al. Histone H3 methylation by Set2 directs deacetylation of coding regions by Rpd3S to suppress spurious intragenic transcription. Cell. 2005;123:581–592. - PubMed
-
- Hampsey M., Reinberg D., Reinberg D. Tails of intrigue: Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II mediates histone methylation. Cell. 2003;113:429–432. - PubMed
-
- Hediger F., Gasser S.M., Gasser S.M. Heterochromatin protein 1: Don’t judge the book by its cover! Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2006;16:143–150. - PubMed
-
- Heetebrij R.J., Talman E.G., van Velzen M.A., van Gijlswijk R.P., Snoeijers S.S., Schalk M., Wiegant J., de van Rijke F., Kerkhoven R.M., Raap A.K., Talman E.G., van Velzen M.A., van Gijlswijk R.P., Snoeijers S.S., Schalk M., Wiegant J., de van Rijke F., Kerkhoven R.M., Raap A.K., van Velzen M.A., van Gijlswijk R.P., Snoeijers S.S., Schalk M., Wiegant J., de van Rijke F., Kerkhoven R.M., Raap A.K., van Gijlswijk R.P., Snoeijers S.S., Schalk M., Wiegant J., de van Rijke F., Kerkhoven R.M., Raap A.K., Snoeijers S.S., Schalk M., Wiegant J., de van Rijke F., Kerkhoven R.M., Raap A.K., Schalk M., Wiegant J., de van Rijke F., Kerkhoven R.M., Raap A.K., Wiegant J., de van Rijke F., Kerkhoven R.M., Raap A.K., de van Rijke F., Kerkhoven R.M., Raap A.K., Kerkhoven R.M., Raap A.K., Raap A.K., et al. Platinum(II)-based coordination compounds as nucleic acid labeling reagents: Synthesis, reactivity, and applications in hybridization assays. ChemBioChem. 2003;4:573–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
