Nerve growth factor stimulates the concentration of TrkA within lipid rafts and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation through c-Cbl-associated protein
- PMID: 17548467
- PMCID: PMC1952120
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01109-06
Nerve growth factor stimulates the concentration of TrkA within lipid rafts and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation through c-Cbl-associated protein
Abstract
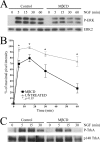
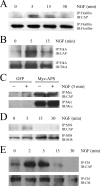
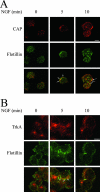
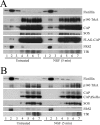
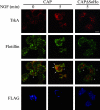
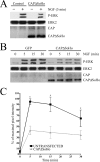
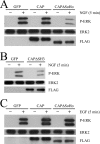
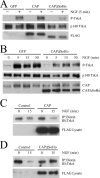
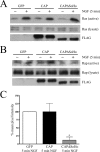
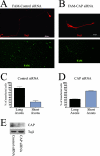
Nerve growth factor (NGF) acts through its receptor, TrkA, to elicit the neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells through the action of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) and ERK2. Upon NGF binding, TrkA translocates and concentrates in cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains or lipid rafts, facilitating formation of receptor-associated signaling complexes, activation of downstream signaling pathways, and internalization into endosomes. We have investigated the mechanisms responsible for the localization of TrkA within lipid rafts and its ability to activate ERK1 and ERK2. We report that NGF treatment results in the translocation of activated forms of TrkA to lipid rafts, and this localization is important for efficient activation of the ERKs. TrkA is recruited and retained within lipid rafts through its association with flotillin, an intrinsic constituent of these membrane microdomains, via the adapter protein, c-Cbl associated protein (CAP). Mutant forms of CAP that lack protein interaction domains block TrkA localization to lipid rafts and attenuate ERK activation. Importantly, suppression of endogenous CAP expression inhibited NGF-stimulated neurite outgrowth from primary dorsal root ganglion neurons. These data provide a mechanism for the lipid raft localization of TrkA and establish the importance of the CAP adaptor protein for NGF activation of the ERKs and neuronal differentiation.
Figures

References
-
- Ahn, M. Y., K. D. Katsanakis, F. Bheda, and T. S. Pillay. 2004. Primary and essential role of the adaptor protein APS for recruitment of both c-Cbl and its associated protein CAP in insulin signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 279:21526-21532. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, R. G. 1998. The caveolae membrane system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67:199-225. - PubMed
-
- Arispe, N., and M. Doh. 2002. Plasma membrane cholesterol controls the cytotoxicity of Alzheimer's disease AbetaP (1-40) and (1-42) peptides. FASEB J. 16:1526-1536. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, C. A., V. Ribon, M. Kanzaki, D. C. Thurmond, S. Mora, S. Shigematsu, P. E. Bickel, J. E. Pessin, and A. R. Saltiel. 2000. CAP defines a second signalling pathway required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. Nature 407:202-207. - PubMed
-
- Bickel, P. E., P. E. Scherer, J. E. Schnitzer, P. Oh, M. P. Lisanti, and H. F. Lodish. 1997. Flotillin and epidermal surface antigen define a new family of caveolae-associated integral membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 272:13793-13802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
