Bound to shock: protection from lethal endotoxemic shock by a novel, nontoxic, alkylpolyamine lipopolysaccharide sequestrant
- PMID: 17548488
- PMCID: PMC1932507
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00200-07
Bound to shock: protection from lethal endotoxemic shock by a novel, nontoxic, alkylpolyamine lipopolysaccharide sequestrant
Abstract
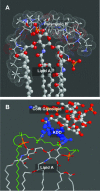
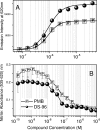
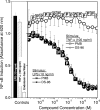
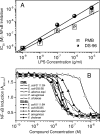
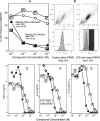
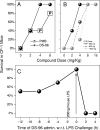
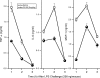
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), or endotoxin, a structural component of gram-negative bacterial outer membranes, plays a key role in the pathogenesis of septic shock, a syndrome of severe systemic inflammation which leads to multiple-system organ failure. Despite advances in antimicrobial chemotherapy, sepsis continues to be the commonest cause of death in the critically ill patient. This is attributable to the lack of therapeutic options that aim at limiting the exposure to the toxin and the prevention of subsequent downstream inflammatory processes. Polymyxin B (PMB), a peptide antibiotic, is a prototype small molecule that binds and neutralizes LPS toxicity. However, the antibiotic is too toxic for systemic use as an LPS sequestrant. Based on a nuclear magnetic resonance-derived model of polymyxin B-LPS complex, we had earlier identified the pharmacophore necessary for optimal recognition and neutralization of the toxin. Iterative cycles of pharmacophore-based ligand design and evaluation have yielded a synthetically easily accessible N(1),mono-alkyl-mono-homologated spermine derivative, DS-96. We have found that DS-96 binds LPS and neutralizes its toxicity with a potency indistinguishable from that of PMB in a wide range of in vitro assays, affords complete protection in a murine model of LPS-induced lethality, and is apparently nontoxic in vertebrate animal models.
Figures
References
-
- Beamer, L. J., S. F. Carroll, and D. Eisenberg. 1999. The three-dimensional structure of human bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein: implications for understanding protein-lipopolysaccharide interactions. Biochem. Pharmacol. (Oxford) 57:225-229. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharjya, S., S. A. David, V. I. Mathan, and P. Balaram. 1997. Polymyxin B nonapeptide: conformations in water and in the lipopolysaccharide-bound state determined by two-dimensional NMR and molecular dynamics. Biopolymers 41:251-265.
-
- Bone, R. C. 1996. The sepsis syndrome. Definition and general approach to management. Clin. Chest Med. 17:175-181. - PubMed
-
- Burns, M. R., S. A. Jenkins, S. J. Wood, K. Miller, and S. A. David. 2006. Structure-activity relationships in lipopolysaccharide neutralizers: design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a 540-membered amphipathic bisamide library. J. Comb. Chem. 8:32-43. - PubMed
-
- Burns, M. R., S. J. Wood, K. A. Miller, T. Nguyen, J. R. Cromer, and S. A. David. 2005. Lysine-spermine conjugates: hydrophobic polyamine amides as potent lipopolysaccharide sequestrants. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13:2523-2536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

