Modulation of the cellular accumulation and intracellular activity of daptomycin towards phagocytized Staphylococcus aureus by the P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter in human THP-1 macrophages and madin-darby canine kidney cells
- PMID: 17548493
- PMCID: PMC1932525
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00090-07
Modulation of the cellular accumulation and intracellular activity of daptomycin towards phagocytized Staphylococcus aureus by the P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter in human THP-1 macrophages and madin-darby canine kidney cells
Abstract
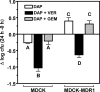
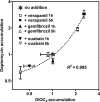
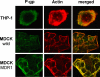
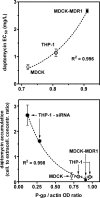
P-glycoprotein (P-gp; MDR1), a major efflux transporter, recognizes various antibiotics and is present in macrophages. We have examined its effect on the modulation of the intracellular accumulation and activity of daptomycin towards phagocytized Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923) in human THP-1 macrophages, in comparison with MDCK epithelial cells (wild type and MDCK-MDR1 overexpressing P-gp; the bulk of the protein was immunodetected at the surface of all three cell types). Daptomycin displayed concentration-dependent intracellular activity (Hill equation pattern) in THP-1 and MDCK cells with (i) 50% effective drug extracellular concentration (EC(50); relative potency) and static concentrations at 9 to 10 times the MIC and (ii) maximal efficacy (E(max); CFU decrease at infinite extracellular drug concentration) at 1.6 to 2 log compared to that of the postphagocytosis inoculum. Verapamil (100 microM) and elacridar (GF 120918; 0.5 microM), two known inhibitors of P-gp, decreased daptomycin EC(50) (about threefold) in THP-1 and MDCK cells without affecting E(max). Daptomycin EC(50) was about three- to fourfold higher and accumulation in MDCK-MDR1 commensurately lower than in wild-type cells. In THP-1 macrophages, (i) verapamil and ATP depletion increased, and ouabain (an inducer of mdr1 [the gene encoding P-gp] expression) decreased the accumulation of daptomycin in parallel with that of DiOC(2) (a known substrate of P-gp); (ii) silencing mdr1 with duplex human mdr1 siRNAs reduced the cell content in immunoreactive P-gp to 15 to 30% of controls and caused an eight- to 13-fold increase in daptomycin accumulation. We conclude that daptomycin is subject to efflux from THP-1 macrophages and MDCK cells by P-gp, which reduces its intracellular activity against phagocytized S. aureus.
Figures


References
-
- Acharya, P., T. T. Tran, J. W. Polli, A. Ayrton, H. Ellens, and J. Bentz. 2006. P-glycoprotein (P-gp) expressed in a confluent monolayer of hMDR1-MDCKII cells has more than one efflux pathway with cooperative binding sites. Biochemistry 45:15505-15519. - PubMed
-
- Andrew, J. H., M. C. Wale, L. J. Wale, and D. Greenwood. 1987. The effect of cultural conditions on the activity of LY146032 against staphylococci and streptococci. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 20:213-221. - PubMed
-
- Barcia-Macay, M., S. Lemaire, M. P. Mingeot-Leclercq, P. M. Tulkens, and F. Van Bambeke. 2006. Evaluation of the extracellular and intracellular activities (human THP-1 macrophages) of telavancin versus vancomycin against methicillin-susceptible, methicillin-resistant, vancomycin-intermediate and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 58:1177-1184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

