MyD88-dependent expansion of an immature GR-1(+)CD11b(+) population induces T cell suppression and Th2 polarization in sepsis
- PMID: 17548519
- PMCID: PMC2118626
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20062602
MyD88-dependent expansion of an immature GR-1(+)CD11b(+) population induces T cell suppression and Th2 polarization in sepsis
Abstract
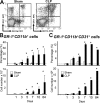
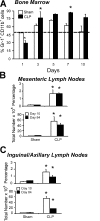
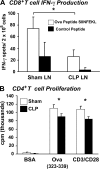
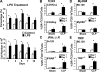
Polymicrobial sepsis alters the adaptive immune response and induces T cell suppression and Th2 immune polarization. We identify a GR-1(+)CD11b(+) population whose numbers dramatically increase and remain elevated in the spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow during polymicrobial sepsis. Phenotypically, these cells are heterogeneous, immature, predominantly myeloid progenitors that express interleukin 10 and several other cytokines and chemokines. Splenic GR-1(+) cells effectively suppress antigen-specific CD8(+) T cell interferon (IFN) gamma production but only modestly suppress antigen-specific and nonspecific CD4(+) T cell proliferation. GR-1(+) cell depletion in vivo prevents both the sepsis-induced augmentation of Th2 cell-dependent and depression of Th1 cell-dependent antibody production. Signaling through MyD88, but not Toll-like receptor 4, TIR domain-containing adaptor-inducing IFN-beta, or the IFN-alpha/beta receptor, is required for complete GR-1(+)CD11b(+) expansion. GR-1(+)CD11b(+) cells contribute to sepsis-induced T cell suppression and preferential Th2 polarization.
Figures



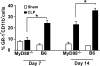
References
-
- Hotchkiss, R.S., and I.E. Karl. 2003. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 348:138–150. - PubMed
-
- Hotchkiss, R.S., K.W. Tinsley, P.E. Swanson, R.E. Schmieg Jr., J.J. Hui, K.C. Chang, D.F. Osborne, B.D. Freeman, J.P. Cobb, T.G. Buchman, and I.E. Karl. 2001. Sepsis-induced apoptosis causes progressive profound depletion of B and CD4+ T lymphocytes in humans. J. Immunol. 166:6952–6963. - PubMed
-
- Oberholzer, C., A. Oberholzer, F.R. Bahjat, R.M. Minter, C.L. Tannahill, A. Abouhamze, D. LaFace, B. Hutchins, M.J. Clare-Salzler, and L.L. Moldawer. 2001. Targeted adenovirus-induced expression of IL-10 decreases thymic apoptosis and improves survival in murine sepsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 98:11503–11508. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murphey, E.D., C.Y. Lin, R.W. McGuire, T. Toliver-Kinsky, D.N. Herndon, and E.R. Sherwood. 2004. Diminished bacterial clearance is associated with decreased IL-12 and interferon-gamma production but a sustained proinflammatory response in a murine model of postseptic immunosuppression. Shock. 21:415–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

