Deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD negatively regulates the ubiquitin-dependent kinase Tak1 and prevents abnormal T cell responses
- PMID: 17548520
- PMCID: PMC2118606
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20062694
Deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD negatively regulates the ubiquitin-dependent kinase Tak1 and prevents abnormal T cell responses
Abstract
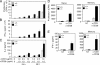
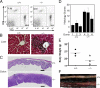
The deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD has recently been implicated in the regulation of signal transduction, but its physiological function and mechanism of action are still elusive. In this study, we show that CYLD plays a pivotal role in regulating T cell activation and homeostasis. T cells derived from Cyld knockout mice display a hyperresponsive phenotype and mediate the spontaneous development of intestinal inflammation. Interestingly, CYLD targets a ubiquitin-dependent kinase, transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (Tak1), and inhibits its ubiquitination and autoactivation. Cyld-deficient T cells exhibit constitutively active Tak1 and its downstream kinases c-Jun N-terminal kinase and IkappaB kinase beta. These results emphasize a critical role for CYLD in preventing spontaneous activation of the Tak1 axis of T cell signaling and, thereby, maintaining normal T cell function.
Figures



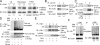
References
-
- Siegel, R.M., M. Katsumata, S. Komori, S. Wadsworth, L. Gill-Morse, S. Jerrold-Jones, A. Bhandoola, M.I. Greene, and K. Yui. 1990. Mechanisms of autoimmunity in the context of T-cell tolerance: insights from natural and transgenic animal model systems. Immunol. Rev. 118:165–192. - PubMed
-
- Liu, Y.C. 2004. Ubiquitin ligases and the immune response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22:81–127. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson, K.D. 2000. Ubiquitination and deubiquitination: targeting of proteins for degradation by the proteasome. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 11:141–148. - PubMed
-
- Reiley, W.W., M. Zhang, W. Jin, M. Losiewicz, K.B. Donohue, C.C. Norbury, and S.C. Sun. 2006. Regulation of T cell development by the deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD. Nat. Immunol. 7:411–417. - PubMed
-
- Bignell, G.R., W. Warren, S. Seal, M. Takahashi, E. Rapley, R. Barfoot, H. Green, C. Brown, P.J. Biggs, S.R. Lakhani, et al. 2000. Identification of the familial cylindromatosis tumour-suppressor gene. Nat. Genet. 25:160–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI064639/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR-15428-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- CA94922/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI057555/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI056094/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 2T32CA60395-11/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI064639/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057555/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA060395/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA094922/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI056094/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI056094/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI064639/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR015428/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

