A novel role for HMGB1 in TLR9-mediated inflammatory responses to CpG-DNA
- PMID: 17548579
- PMCID: PMC1976374
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-09-044776
A novel role for HMGB1 in TLR9-mediated inflammatory responses to CpG-DNA
Abstract
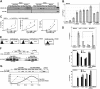
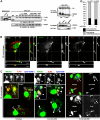
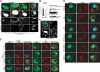
CpG-DNA or its synthetic analog CpG-ODN activates innate immunity through Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9). However, the mechanism of TLR9 activation by CpG-DNA remains elusive. Here we have identified HMGB1 as a CpG-ODN-binding protein. HMGB1 interacts and preassociates with TLR9 in the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC), and hastens TLR9's redistribution to early endosomes in response to CpG-ODN. CpG-ODN stimulates macrophages and dendritic cells to secrete HMGB1; in turn, extracellular HMGB1 accelerates the delivery of CpG-ODNs to its receptor, leading to a TLR9-dependent augmentation of IL-6, IL-12, and TNFalpha secretion. Loss of HMGB1 leads to a defect in the IL-6, IL-12, TNFalpha, and iNOS response to CpG-ODN. However, lack of intracellular TLR9-associated HMGB1 can be compensated by extracellular HMGB1. Thus, the DNA-binding protein HMGB1 shuttles in and out of immune cells and regulates inflammatory responses to CpG-DNA.
Figures




References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:675–680. - PubMed
-
- Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:335–376. - PubMed
-
- Razin A, Friedman J. DNA methylation and its possible biological roles. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;25:33–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

