Fragile X mental retardation protein FMRP and the RNA export factor NXF2 associate with and destabilize Nxf1 mRNA in neuronal cells
- PMID: 17548835
- PMCID: PMC1891223
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700169104
Fragile X mental retardation protein FMRP and the RNA export factor NXF2 associate with and destabilize Nxf1 mRNA in neuronal cells
Abstract
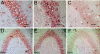
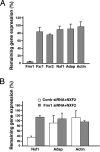
Fragile X syndrome is caused by the inactivation of the X-linked FMR1 gene, leading to the loss of its encoded protein FMRP. Although macroorchidism and defects in neuronal architecture and function have been associated with lack of FMRP, the exact molecular mechanism underlying this disease remains unclear. We have reported previously that in the brain and testis of mice, FMRP specifically interacts with a distinct mRNA nuclear export factor NXF2 but not with its close relative NXF1, a ubiquitously expressed essential mRNA nuclear export factor. This interaction marked NXF2 as a putative functional partner of FMRP. Here, we demonstrate by immunoprecipitation and quantitative real-time RT-PCR that, in cultured mouse neuronal cells, both FMRP and NXF2 are present in Nxf1 mRNA-containing ribonucleoprotein particles. Further, we show that expression of NXF2 leads to the destabilization of Nxf1 mRNA and that this effect is abolished when Fmr1 expression is reduced by siRNA, arguing that both proteins collaborate to exert this effect. Importantly, these findings correlate well with our observations that in both mouse hippocampal neurons and male germ cells where the expression of FMRP and NXF2 is most prominent, the expression of NXF1 is relatively poorly expressed. Our studies thus identify Nxf1 mRNA as a likely biologically relevant in vivo target of both FMRP and NXF2 and implicate FMRP, in conjunction with NXF2, as a posttranscriptional regulator of a major mRNA export factor. Such regulation may prove important in the normal development and function of neurons as well as of male germ cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bardoni B, Davidovic L, Bensaid M, Khandjian EW. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2006;8:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Koukoui SD, Chaudhuri A. Brain Res Rev. 2006;53:27–38. - PubMed
-
- Devys D, Lutz Y, Rouyer N, Bellocq JP, Mandel JL. Nat Genet. 1993;4:335–340. - PubMed
-
- Bakker CE, Otero Y, Bontekoe C, Raghoe P, Luteijn T, Hoogeveen AT, Oostra BA, Willemsen R. Exp Cell Res. 2000;258:162–170. - PubMed
-
- Willemsen R, Oostra BA, Bassell GJ, Dictenberg J. Ment Retard Dev Disabil. 2004;10:60–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

