The hypoxia-inducible factor alpha pathway couples angiogenesis to osteogenesis during skeletal development
- PMID: 17549257
- PMCID: PMC1878533
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI31581
The hypoxia-inducible factor alpha pathway couples angiogenesis to osteogenesis during skeletal development
Abstract
Skeletal development and turnover occur in close spatial and temporal association with angiogenesis. Osteoblasts are ideally situated in bone to sense oxygen tension and respond to hypoxia by activating the hypoxia-inducible factor alpha (HIF alpha) pathway. Here we provide evidence that HIF alpha promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis by elevating VEGF levels in osteoblasts. Mice overexpressing HIF alpha in osteoblasts through selective deletion of the von Hippel-Lindau gene (Vhl) expressed high levels of Vegf and developed extremely dense, heavily vascularized long bones. By contrast, mice lacking Hif1a in osteoblasts had the reverse skeletal phenotype of that of the Vhl mutants: long bones were significantly thinner and less vascularized than those of controls. Loss of Vhl in osteoblasts increased endothelial sprouting from the embryonic metatarsals in vitro but had little effect on osteoblast function in the absence of blood vessels. Mice lacking both Vhl and Hif1a had a bone phenotype intermediate between those of the single mutants, suggesting overlapping functions of HIFs in bone. These studies suggest that activation of the HIF alpha pathway in developing bone increases bone modeling events through cell-nonautonomous mechanisms to coordinate the timing, direction, and degree of new blood vessel formation in bone.
Figures
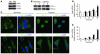
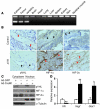

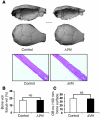

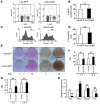

Comment in
-
Vascular biology and bone formation: hints from HIF.J Clin Invest. 2007 Jun;117(6):1477-80. doi: 10.1172/JCI32518. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17549250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinbrech D.S., et al. VEGF expression in an osteoblast-like cell line is regulated by a hypoxia response mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2000;278:C853–C860. - PubMed
-
- Semenza G.L. Regulation of mammalian O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. . Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999;15:551–578. - PubMed
-
- Semenza G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: oxygen homeostasis and disease pathophysiology. Trends Mol. Med. 2001;7:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Kaelin W.G., Jr. Molecular basis of the VHL hereditary cancer syndrome. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:673–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

