RNA interference-mediated targeting of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression in the IOMM-lee malignant meningioma cell line inhibits tumor growth, tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis
- PMID: 17549400
- PMCID: PMC1937039
RNA interference-mediated targeting of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression in the IOMM-lee malignant meningioma cell line inhibits tumor growth, tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis
Abstract
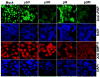
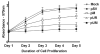
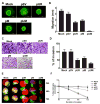
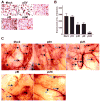
Meningiomas are the most commonly occurring tumors of the central nervous system including the brain and spinal cord. Malignant meningiomas are highly aggressive and frequently recur after surgical resection of the tumor. Our previous studies have reported that urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) play important roles in tumor progression. In the present study, we have attempted to evaluate the roles of these molecules in the malignant meningioma tumor microenvironment and to determine the effectiveness of using single or bicistronic small interfering RNA constructs for uPAR and MMP-9 on tumor cell proliferation, migration, invasion, angiogenesis and regression of pre-established orthotopic tumors. Transfection of single or bicistronic constructs downregulated uPAR and MMP-9 in meningioma cells compared to controls. A significant reduction in tumor invasion was determined with matrigel gel and spheroid invasion assays in meningioma cells after transfection of these plasmids. Furthermore, downregulation of uPAR and MMP-9 reduced migration of tumor spheroids on vitronectin-coated plates. uPAR and MMP-9 downregulation suppressed capillary network formation, in both in vitro and in vivo models. Also, it is well known that tumor cells manipulate intracellular signaling pathways to aid in various processes involved in tumor progression. Our study revealed that downregulation of uPAR and MMP-9 leads to a decrease in the activation of some of the important enzymes participating in the MAPK and PI3 kinase pathways, which in turn, might decrease cell survival and proliferation. In addition, we analyzed the efficiency of RNAi-mediated targeting of uPAR and MMP-9 in pre-established tumor growth in vivo. We observed a significant regression of pre-established orthotopic tumors upon RNAi-mediated targeting of uPAR and MMP-9. In addition, the present study indicated that targeting both the proteins simultaneously augmented the therapeutic treatment of human meningiomas.
Figures


References
-
- Bianchini F, D’Alessio S, Fibbi G, Del RM, Calorini L. Cytokine-dependent invasiveness in B16 murine melanoma cells: role of uPA system and MMP-9. Oncol Rep. 2006;15:709–714. - PubMed
-
- Puli S, Lai JC, Bhushan A. Inhibition of matrix degrading enzymes and invasion in human glioblastoma (U87MG) Cells by isoflavones. J Neurooncol. 2006;79:135–142. - PubMed
-
- Schwab W, Schulze-Tanzil G, Mobasheri A, Dressler J, Kotzsch M, Shakibaei M. Interleukin-1beta-induced expression of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor and its co-localization with MMPs in human articular chondrocytes. Histol Histopathol. 2004;19:105–112. - PubMed
-
- Tan X, Egami H, Nozawa F, Abe M, Baba H. Analysis of the invasion-metastasis mechanism in pancreatic cancer: involvement of plasmin(ogen) cascade proteins in the invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2006;28:369–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

