Selected flavonoids potentiate the toxicity of cisplatin in human lung adenocarcinoma cells: a role for glutathione depletion
- PMID: 17549417
- PMCID: PMC3983955
Selected flavonoids potentiate the toxicity of cisplatin in human lung adenocarcinoma cells: a role for glutathione depletion
Abstract
Adjuvant therapies that enhance the anti-tumor effects of cis-diammineplatinum(II) dichloride (cisplatin, CDDP) are actively being pursued. Growing evidence supports the involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction in the anti-cancer effect of cisplatin. We examined the potential of using selective flavonoids that are effective in depleting tumor cells of glutathione (GSH) to potentiate cisplatin-mediated cytotoxicity in human lung adenocarcinoma (A549) cells. We found that cisplatin (40 microM, 48-h treatment) disrupts the steady-state levels of mitochondrial respiratory complex I, which correlates with elevated mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and cytochrome c release. The flavonoids, 2',5'-dihydroxychalcone (2',5'-DHC, 20 microM) and chrysin (20 microM) potentiated the cytotoxicity of cisplatin (20 microM), which could be blocked by supplementation of the media with exogenous GSH (500 microM). Both 2',5'-DHC and chrysin were more effective than the specific inhibitor of GSH synthesis, L-buthionine sulfoximine (BSO, 20 microM), in inducing GSH depletion and potentiating the cytotoxic effect of cisplatin. These data suggest that the flavonoid-induced potentiation of cisplatin's toxicity is due, in part, to synergetic pro-oxidant effects of cisplatin by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction, and the flavonoids by depleting cellular GSH, an important antioxidant defense.
Figures
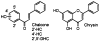

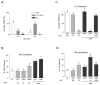


References
-
- Wang D, Lippard SJ. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:307–320. - PubMed
-
- Yen HC, Tang YC, Chen FY, Chen SW, Majima HJ. Enhancement of cisplatin-induced apoptosis and caspase 3 activation by depletion of mitochondrial DNA in a human osteosarcoma cell line. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2005;1042:516–522. - PubMed
-
- Schweyer S, Soruri A, Heintze A, Radzun HJ, Fayyazi A. The role of reactive oxygen species in cisplatin-induced apo-ptosis in human malignant testicular germ cell lines. Int J Oncol. 2004;25:1671–1676. - PubMed
-
- Huang HL, Fang LW, Lu SP, Chu CK, Luh TY, Lai MZ. DNA-damaging reagents induce apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-dependent Fas aggregation. Oncogene. 2003;22:8168–8177. - PubMed
-
- Troyano A, Sancho P, Fernandez C, De Blas E, Bernardi P, Aller P. The selection between apoptosis and necrosis is differentially regulated in hydrogen peroxide-treated and glu-tathione-depleted human promonocytic cells. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10:889–898. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

