Resveratrol is a class IA phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor
- PMID: 17550345
- PMCID: PMC2049032
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070236
Resveratrol is a class IA phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor
Abstract
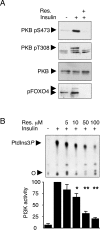
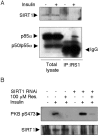
Resveratrol, a polyphenol found in fruits, possesses chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic properties and has been shown to increase lifespan in yeast and metazoans, including mice. Genetic evidence and in vitro enzymatic measurements indicate that the deacetylase Sir2/SIRT1, an enzyme promoting stress resistance and aging, is the target of resveratrol. Similarly, down-regulation of insulin-like pathways, of which PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase) is a key mediator, promotes longevity and is an attractive strategy to fight cancer. We show here that resveratrol inhibits, in vitro and in cultured muscle cell lines, class IA PI3K and its downstream signalling at the same concentration range at which it activates sirtuins. Our observations define class IA PI3K as a target of resveratrol that may contribute to the longevity-promoting and anticancer properties and identify resveratrol as a natural class-specific PI3K inhibitor.
Figures





References
-
- Baur J. A., Sinclair D. A. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006;5:493–506. - PubMed
-
- Jang M., Cai L., Udeani G. O., Slowing K. V., Thomas C. F., Beecher C. W., Fong H. H., Farnsworth N. R., Kinghorn A. D., Mehta R. G., et al. Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes. Science. 1997;275:218–220. - PubMed
-
- Faber A. C., Dufort F. J., Blair D., Wagner D., Roberts M. F., Chiles T. C. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-mediated glucose metabolism coincides with resveratrol-induced cell cycle arrest in human diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006;72:1246–1256. - PubMed
-
- Yang T., Fu M., Pestell R., Sauve A. A. SIRT1 and endocrine signaling. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2006;17:186–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

