Inactivation of viruses by coherent excitations with a low power visible femtosecond laser
- PMID: 17550590
- PMCID: PMC1899485
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-4-50
Inactivation of viruses by coherent excitations with a low power visible femtosecond laser
Abstract
Background: Resonant microwave absorption has been proposed in the literature to excite the vibrational states of microorganisms in an attempt to destroy them. But it is extremely difficult to transfer microwave excitation energy to the vibrational energy of microorganisms due to severe absorption of water in this spectral range. We demonstrate for the first time that, by using a visible femtosecond laser, it is effective to inactivate viruses such as bacteriophage M13 through impulsive stimulated Raman scattering.
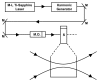
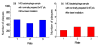
Results and discussion: By using a very low power (as low as 0.5 nj/pulse) visible femtosecond laser having a wavelength of 425 nm and a pulse width of 100 fs, we show that M13 phages were inactivated when the laser power density was greater than or equal to 50 MW/cm2. The inactivation of M13 phages was determined by plaque counts and had been found to depend on the pulse width as well as power density of the excitation laser.
Conclusion: Our experimental findings lay down the foundation for an innovative new strategy of using a very low power visible femtosecond laser to selectively inactivate viruses and other microorganisms while leaving sensitive materials unharmed by manipulating and controlling with the femtosecond laser system.
Figures


References
-
- Ford LH. Estimate of the vibrational frequencies of spherical virus particles. Phys Rev. 2003. E67, 051924-1-051924-3. - PubMed
-
- Tsen KT, Dykeman EC, Sankey OF, Lin N-T, Tsen S-WD, Kiang JG. Raman scattering studies of the low-frequency vibrational modes of bacteriophage M13 in water -observation of an axial torsion mode. Nanotechnology. 2006;17:5474–5479. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/17/21/030. - DOI
-
- Yan Y-X, Gamble EB, Jr, Nelson KA. Impulsive stimulated scattering:General importance in femtosecond laser pulse interactions with matter, and spectroscopic applications. J Chem Phys. 1985;83:5391–5399. doi: 10.1063/1.449708. - DOI
-
- Tsen KT. Ultrafast Physical processes in semiconductors, edited by KT Tsen, Vol 67 in the series – semiconductors and Semimetals. Academic Press, New York; 2001. Ultrafast dynamics in wide bandgap wurtzite GaN; pp. 109–149.
-
- Tsen KT. Electron velocity overshoot, ballistic electron transport and non-equilibrium phonon dynamics in nanostructure semiconductors. In: Tsen KT, editor. Ultrafast Phenomena in Semiconductors. Springer-Verlag NY; 2001. pp. 191–259.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

